Microbial Fuel Cell Construction Features and Application for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment
- PMID: 37233551
- PMCID: PMC10223362
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes13050490
Microbial Fuel Cell Construction Features and Application for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
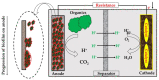
A microbial fuel cell (MFC) is a system that can generate electricity by harnessing microorganisms' metabolic activity. MFCs can be used in wastewater treatment plants since they can convert the organic matter in wastewater into electricity while also removing pollutants. The microorganisms in the anode electrode oxidize the organic matter, breaking down pollutants and generating electrons that flow through an electrical circuit to the cathode compartment. This process also generates clean water as a byproduct, which can be reused or released back into the environment. MFCs offer a more energy-efficient alternative to traditional wastewater treatment plants, as they can generate electricity from the organic matter in wastewater, offsetting the energy needs of the treatment plants. The energy requirements of conventional wastewater treatment plants can add to the overall cost of the treatment process and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. MFCs in wastewater treatment plants can increase sustainability in wastewater treatment processes by increasing energy efficiency and reducing operational cost and greenhouse gas emissions. However, the build-up to the commercial-scale still needs a lot of study, as MFC research is still in its early stages. This study thoroughly describes the principles underlying MFCs, including their fundamental structure and types, construction materials and membrane, working mechanism, and significant process elements influencing their effectiveness in the workplace. The application of this technology in sustainable wastewater treatment, as well as the challenges involved in its widespread adoption, are discussed in this study.
Keywords: MFCs; construction features; membrane; sustainable; wastewater.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Roy H., Islam M.S., Arifin M.T., Firoz S.H. Chitosan-ZnO Decorated Moringa Oleifera Seed Biochar for Sequestration of Methylene Blue: Isotherms, Kinetics, and Response Surface Analysis. Environ. Nanotech. Monit. Manag. 2022;18:100752. doi: 10.1016/j.enmm.2022.100752. - DOI
-
- Jahan N., Tahmid M., Shoronika A.Z., Fariha A., Roy H., Pervez M.N., Cai Y., Naddeo V., Islam M.S. A Comprehensive Review on the Sustainable Treatment of Textile Wastewater: Zero Liquid Discharge and Resource Recovery Perspectives. Sustainability. 2022;14:15398. doi: 10.3390/su142215398. - DOI
-
- Rahman T.U., Roy H., Islam M.R., Tahmid M., Fariha A., Mazumder A., Tasnim N., Pervez M.N., Cai Y., Naddeo V., et al. The Advancement in Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Technology toward Sustainable Industrial Wastewater Management. Membranes. 2023;13:181. doi: 10.3390/membranes13020181. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colantonio N. Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater Using Microbial Electrolysis Cells. McMaster University; Hamilton, Canada: 2016.
-
- Kurniawan T.A., Chan G.Y.S., Lo W.H., Babel S. Physico–Chemical Treatment Techniques for Wastewater Laden with Heavy Metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2006;118:83–98. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2006.01.015. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

