Modeling breast cancer proliferation, drug synergies, and alternating therapies
- PMID: 37234088
- PMCID: PMC10206440
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106714
Modeling breast cancer proliferation, drug synergies, and alternating therapies
Abstract
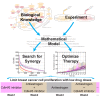
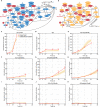
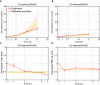
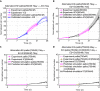
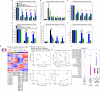
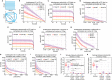
Estrogen receptor positive (ER+) breast cancer is responsive to a number of targeted therapies used clinically. Unfortunately, the continuous application of targeted therapy often results in resistance, driving the consideration of combination and alternating therapies. Toward this end, we developed a mathematical model that can simulate various mono, combination, and alternating therapies for ER + breast cancer cells at different doses over long time scales. The model is used to look for optimal drug combinations and predicts a significant synergism between Cdk4/6 inhibitors in combination with the anti-estrogen fulvestrant, which may help explain the clinical success of adding Cdk4/6 inhibitors to anti-estrogen therapy. Furthermore, the model is used to optimize an alternating treatment protocol so it works as well as monotherapy while using less total drug dose.
Keywords: Cancer; Cancer systems biology; Computational bioinformatics; Mathematical biosciences; Pharmacoinformatics.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
WEE1 inhibition delays resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor and antiestrogen treatment in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 19:2024.09.15.613122. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.15.613122. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345487 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Estrogen Down-regulator Fulvestrant Potentiates Antitumor Activity of Fluoropyrimidine in Estrogen-responsive MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells.In Vivo. 2019 Sep-Oct;33(5):1439-1445. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11622. In Vivo. 2019. PMID: 31471390 Free PMC article.
-
Elacestrant (RAD1901) exhibits anti-tumor activity in multiple ER+ breast cancer models resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 18;21(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1230-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31852484 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Fulvestrant in Breast Cancer.Oncol Ther. 2017;5(1):17-29. doi: 10.1007/s40487-017-0046-2. Epub 2017 May 8. Oncol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28680952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to selective estrogen receptor down-regulator in metastatic breast cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017 Aug;1868(1):148-156. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.03.008. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28344099 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic modeling of cell viability assays with in silico lineage tracing.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 26:2024.08.23.609433. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.23.609433. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39253474 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
WEE1 inhibition delays resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor and antiestrogen treatment in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 19:2024.09.15.613122. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.15.613122. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345487 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Personalized cancer treatment strategies incorporating irreversible and reversible drug resistance mechanisms.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2025 Jul 3;11(1):70. doi: 10.1038/s41540-025-00547-5. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2025. PMID: 40610469 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

