A cell transmembrane peptide chimeric M(27-39)-HTPP targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37234089
- PMCID: PMC10205784
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106766
A cell transmembrane peptide chimeric M(27-39)-HTPP targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
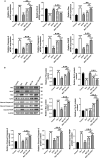
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a prevalent malignant tumor, with a growing incidence and death rate worldwide. The aims and challenges of treating HCC include targeting the tumor, entering the tumor tissue, inhibiting the spread and growth of tumor cells. M27-39 is a small peptide isolated from the antimicrobial peptide Musca domestica cecropin (MDC), whereas HTPP is a liver-targeting, cell-penetrating peptide obtained from the circumsporozoite protein (CSP) of Plasmodium parasites. In this study, M27-39 was modified by HTPP to form M(27-39)-HTPP, which targeted tumor penetration to treat HCC. Here, we revealed that M(27-39)-HTPP had a good ability to target and penetrate the tumor, effectively limit the proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induce the apoptosis in HCC. Notably, M(27-39)-HTPP demonstrated good biosecurity when administered at therapeutic doses. Accordingly, M(27-39)-HTPP could be used as a new, safe, and efficient therapeutic peptide for HCC.
Keywords: Cancer; Chemistry; Oncology.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The patent in question is held by X.L./Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, ZhaoXia Chen, S.G., Lun Zhang, Along Liu, Yanan Tang, Jie Wang, Wenbin Liu, X.J., Jiayong Zhu. (Patent No. ZL201810196235.0). The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Xu J., Cheng X., Tan L., Fu C., Ahmed M., Tian J., Dou J., Zhou Q., Ren X., Wu Q., et al. Microwave responsive nanoplatform via P-selectin mediated drug delivery for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with distant metastasis. Nano Lett. 2019;19:2914–2927. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b05202. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

