Photoactivated Artificial Molecular Motors
- PMID: 37234111
- PMCID: PMC10207102
- DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00089
Photoactivated Artificial Molecular Motors
Abstract
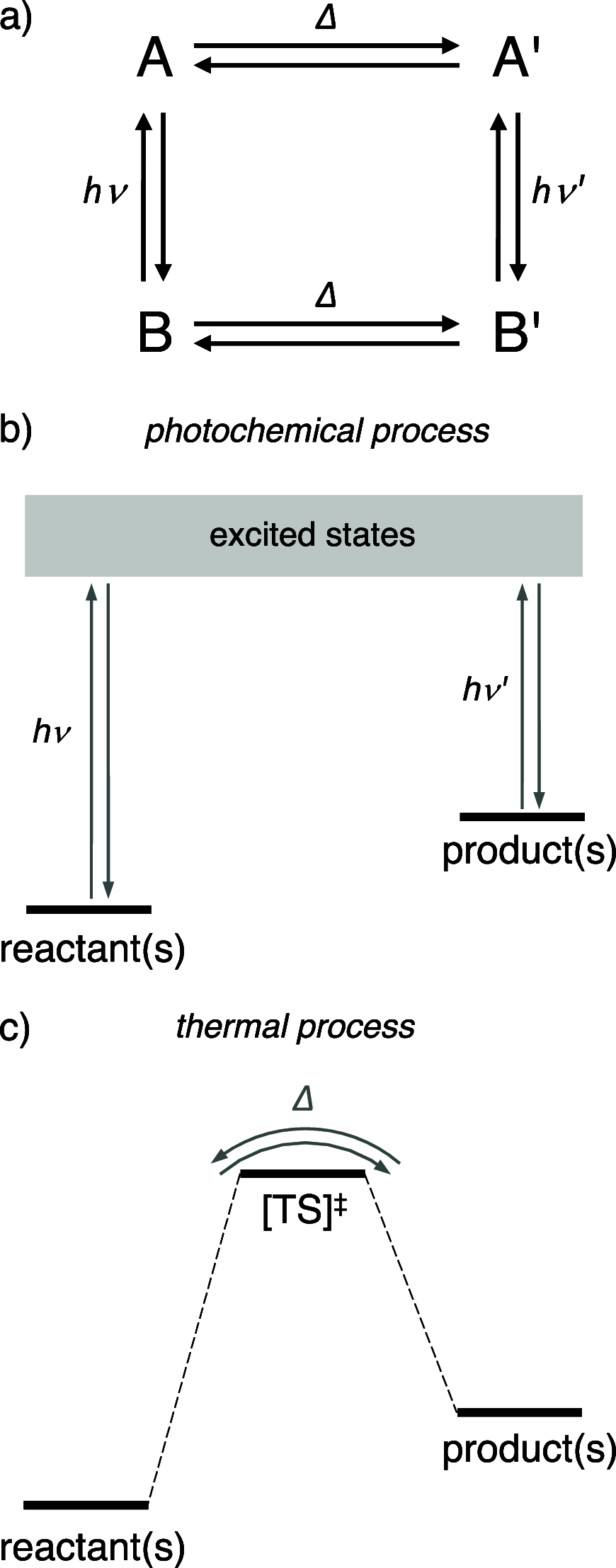
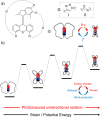
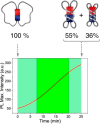
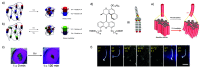
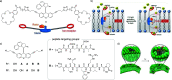
Accurate control of long-range motion at the molecular scale holds great potential for the development of ground-breaking applications in energy storage and bionanotechnology. The past decade has seen tremendous development in this area, with a focus on the directional operation away from thermal equilibrium, giving rise to tailored man-made molecular motors. As light is a highly tunable, controllable, clean, and renewable source of energy, photochemical processes are appealing to activate molecular motors. Nonetheless, the successful operation of molecular motors fueled by light is a highly challenging task, which requires a judicious coupling of thermal and photoinduced reactions. In this paper, we focus on the key aspects of light-driven artificial molecular motors with the aid of recent examples. A critical assessment of the criteria for the design, operation, and technological potential of such systems is provided, along with a perspective view on future advances in this exciting research area.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


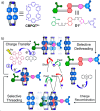
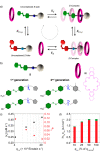
References
-
- Goodsell D. S.The Machinery of Life; Copernicus, 2009.
-
- Rao R.; Esposito M. Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics of Chemical Reaction Networks: Wisdom from Stochastic Thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. X 2016, 6, 04106410.1103/PhysRevX.6.041064. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
