Effects of the mTOR Pathway on the Balance of Th2/Treg Cells in Children with Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome
- PMID: 37234433
- PMCID: PMC10208544
- DOI: 10.4103/ijn.ijn_521_21
Effects of the mTOR Pathway on the Balance of Th2/Treg Cells in Children with Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome
Abstract
Introduction: Immune dysfunction contributes to the progression of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS), but the details of the pathogenesis of progression remain unknown. This study of children with INS investigated the relationship of activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway (PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K) with the levels of T helper 2/regulatory T (Th2/Treg) cells.
Materials and methods: Twenty children with active INS (before steroid treatment), 20 children with remitting INS (INS-R, after steroid treatment), and 20 healthy control children (Ctrl) were enrolled. The levels of Th2/Treg cells in their peripheral circulatory systems were measured using flow cytometry, and the concentration of interleukin (IL)-4 was determined using a cytometric bead array (CBA). The levels of PI3K, AKT, mTOR, p70S6K, and transcription factors associated with Th2/Treg cells were measured using real-time polymerase chain reaction.
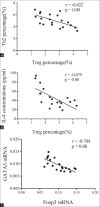
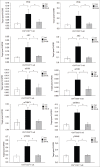
Results: The INS group had a greater proportion of circulating Th2 cells; level of IL-4 protein; and levels of GATA, PI3K, AKT, mTOR, and p70S6K mRNAs than the Ctrl group (all P < 0.05), but a lower proportion of circulating Tregs and expression of Foxp3 (both P < 0.05). Patients in the INS-R group had normalization of these markers (all P < 0.05). Patients in the INS group had negative correlation in the percentage of Treg cells with Th2 cells and with IL-4 level and a negative correlation in the levels of GATA3 and Foxp3 mRNAs.
Conclusions: Patients with active INS had an imbalance of Th2/Treg cells, which might result from the aberrant signaling of the mTOR pathway (PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K).
Keywords: Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome; Th2 cells; Treg cells; mTOR pathway.
Copyright: © 2023 Indian Journal of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yang JY, Yao Y. [Analysis of 1268 patients with chronic renal failure in childhood: A report from 91 hospitals in China from 1990 to 2002] Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2004;42:724–30. - PubMed
-
- Colucci M, Corpetti G, Emma F, Vivarelli M. Immunology of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018;33:573–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
