Nearly maximal information gain due to time integration in central dogma reactions
- PMID: 37235057
- PMCID: PMC10206154
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106767
Nearly maximal information gain due to time integration in central dogma reactions
Abstract
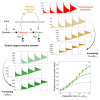
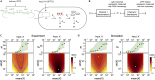
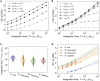
Living cells process information about their environment through the central dogma processes of transcription and translation, which drive the cellular response to stimuli. Here, we study the transfer of information from environmental input to the transcript and protein expression levels. Evaluation of both experimental and analogous simulation data reveals that transcription and translation are not two simple information channels connected in series. Instead, we demonstrate that the central dogma reactions often create a time-integrating information channel, where the translation channel receives and integrates multiple outputs from the transcription channel. This information channel model of the central dogma provides new information-theoretic selection criteria for the central dogma rate constants. Using the data for four well-studied species we show that their central dogma rate constants achieve information gain because of time integration while also keeping the loss because of stochasticity in translation relatively low ( bits).
Keywords: Biophysics; Gene process; Information system model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. This research was conducted when both authors were employed at the National Institute of Standards and Technology. S.S. is currently employed at the Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center. J.R. is currently employed at Booz Allen Hamilton. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, opinion, or position of their current employers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigation of Compatibility between DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation for in Vitro Central Dogma.ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Jun 16;12(6):1813-1822. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00130. Epub 2023 Jun 4. ACS Synth Biol. 2023. PMID: 37271965
-
Optimizing in vitro expression balance of central dogma-related genes using parallel reaction monitoring.J Biosci Bioeng. 2024 Aug;138(2):97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2024.04.006. Epub 2024 May 18. J Biosci Bioeng. 2024. PMID: 38762340
-
The Central Dogma revisited: Insights from protein synthesis, CRISPR, and beyond.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022 Sep;13(5):e1718. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1718. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022. PMID: 35199457
-
Emerging issues of connexin channels: biophysics fills the gap.Q Rev Biophys. 2001 Aug;34(3):325-472. doi: 10.1017/s0033583501003705. Q Rev Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11838236 Review.
-
Vaccinia Virus as a Master of Host Shutoff Induction: Targeting Processes of the Central Dogma and Beyond.Pathogens. 2020 May 21;9(5):400. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050400. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32455727 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

