Recommendations for terminology and the identification of neuropathic pain in people with spine-related leg pain. Outcomes from the NeuPSIG working group
- PMID: 37235637
- PMCID: PMC10348639
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002919
Recommendations for terminology and the identification of neuropathic pain in people with spine-related leg pain. Outcomes from the NeuPSIG working group
Abstract
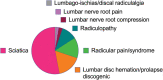
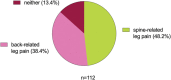
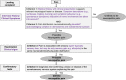
Pain radiating from the spine into the leg is commonly referred to as "sciatica," "Sciatica" may include various conditions such as radicular pain or painful radiculopathy. It may be associated with significant consequences for the person living with the condition, imposing a reduced quality of life and substantial direct and indirect costs. The main challenges associated with a diagnosis of "sciatica" include those related to the inconsistent use of terminology for the diagnostic labels and the identification of neuropathic pain. These challenges hinder collective clinical and scientific understanding regarding these conditions. In this position paper, we describe the outcome of a working group commissioned by the Neuropathic Pain Special Interest Group (NeuPSIG) of the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) which was tasked with the following objectives: (1) to revise the use of terminology for classifying spine-related leg pain and (2) to propose a way forward on the identification of neuropathic pain in the context of spine-related leg pain. The panel recommended discouraging the term "sciatica" for use in clinical practice and research without further specification of what it entails. The term "spine-related leg pain" is proposed as an umbrella term to include the case definitions of somatic referred pain and radicular pain with and without radiculopathy. The panel proposed an adaptation of the neuropathic pain grading system in the context of spine-related leg pain to facilitate the identification of neuropathic pain and initiation of specific management in this patient population.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the International Association for the Study of Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
A. B. Schmid receives grant funding from charities (Wellcome Trust, Medical Research Foundation, Versus Arthritis), government (UKRI, NIHR), and industry (ONO pharmaceutical). She receives lecture fees for postgraduate teaching in peripheral neuropathies and neuropathic pain. B. Tampin receives grant funding from the Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital and Osborne Park Health Care Group Research Advisory Committee and the Charlies Foundation for Research. H. Slater receives grant funding from the Australian Government (Commonwealth), the NH&MRC (MRFF), and Government of WA, Department of Health. R. Baron receives grant support from EU Projects: “Europain” (115007). DOLORisk (633491). IMI Paincare (777500). German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF): Verbundprojekt: Frühdetektion von Schmerzchronifizierung (NoChro) (13GW0338C). German Research Network on Neuropathic Pain (01EM0903). Pfizer Pharma GmbH, Genzyme GmbH, Grünenthal GmbH, Mundipharma Research GmbH und Co. KG., Novartis Pharma GmbH, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc., Zambon GmbH, Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH. He received speaker fees from Pfizer Pharma GmbH, Genzyme GmbH, Grünenthal GmbH, Mundipharma, Sanofi Pasteur, Medtronic Inc. Neuromodulation, Eisai Co.Ltd., Lilly GmbH, Boehringer Ingel-heim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG, Astellas Pharma GmbH, Desitin Arzneimittel GmbH, Teva GmbH, Bayer-Schering, MSD GmbH, Seqirus Australia Pty. Ltd, Novartis Pharma GmbH, TAD Pharma GmbH, Grünenthal SA Portugal, Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH, Agentur Brigitte Süss, Grünenthal Pharma AG Schweiz, Grünenthal B.V. Niederlande, Evapharma, Takeda Pharmaceuticals International AG Schweiz, Ology Medical Education Netherlands. Ralf Baron received consultancy fees from Pfizer Pharma GmbH, Genzyme GmbH, Grünenthal GmbH, Mundipharma Research GmbH und Co. KG, Allergan, Sanofi Pasteur, Medtronic, Eisai, Lilly GmbH, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH&Co.KG, Astellas Pharma GmbH, Novartis Pharma GmbH, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Biogenidec, AstraZeneca GmbH, Merck, Abbvie, Daiichi Sankyo, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals S.A., Seqirus Australia Pty. Ltd, Teva Pharmaceuticals Europe Niederlande, Teva GmbH, Genentech, Mundipharma International Ltd. UK, Astellas Pharma Ltd. UK, Galapagos NV, Kyowa Kirin GmbH, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc., Biotest AG, Celgene GmbH, Desitin Arzneimittel GmbH, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Theranexus DSV CEA Frankreich, Abbott Pro-ducts Operations AG Schweiz, Bayer AG, Grünenthal Pharma AG Schweiz, Mundipharma Research Ltd. UK, Akcea Therapeutics Germany GmbH, Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG, Air Liquide Sante Inter-national Frankreich, Alnylam Germany GmbH, Lateral Pharma Pty Ltd, Hexal AG, An-gelini, Janssen, SIMR Biotech Pty Ltd Australien, Confo Therapeutics N. V. Belgium. N. B. Finnerup Outside the submitted work, NBF reports personal fees from Almirall, NeuroPN, Novartis Pharma, Vertex, and Nanobiotix and has undertaken consultancy work for Aarhus University for Biogen, Merz, and Confo Therapeutics, outside the submitted work and has received a grant from IMI2PainCare an EU IMI 2 (Innovative Medicines Initiative) public–private consortium and the companies involved are: Grünenthal, Bayer, Eli Lilly, Esteve, and Teva, outside the submitted work. P. Hansson declares no conflict of interest. K. Konstantinou declares no conflict of interest. C. Lin declares no conflict of interest. C. Price declares no conflict of interest. B. H. Smith was lead clinician for Chronic Pain for the Scottish Government (2014-2021) and receives grant funding from the Scottish Government, Eli Lilly, and UKRI/Versus Arthritis (not directly related to this work). A. Hietaharju received payment for lectures from Pfizer, Teva, Sanofi, and Lundbeck. Aki Hietaharju was the Chair of the NeuPSIG Executive Committee (2020-2022). J. Markman receives grant support from the National Institutes of Health. J. Markman received consultancy fees from Grunenthal, Merck AG, Eliem, Pfizer, Tremeau, Swan Bio, Nektar, Editas, Grunenthal, Biogen, Lilly, and Lateral Pharma. John Markman has served on Data Safety Monitoring Boards for Regenacy, Tonix, and Novartis pharmaceuticals. John Markman has equity in Yellowblack corporation and has served on the boards of Flowonix Corporation and the North American Neuromodulation Society.
Figures


References
-
- Baron R, Maier C, Attal N, Binder A, Bouhassira D, Cruccu G, Finnerup NB, Haanpaa M, Hansson P, Hullemann P, Jensen TS, Freynhagen R, Kennedy JD, Magerl W, Mainka T, Reimer M, Rice AS, Segerdahl M, Serra J, Sindrup S, Sommer C, Tolle T, Vollert J, Treede RD. Peripheral neuropathic pain: a mechanism-related organizing principle based on sensory profiles. PAIN 2017;158:261–72. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benditz A, Sprenger S, Rauch L, Weber M, Grifka J, Straub RH. Increased pain and sensory hyperinnervation of the ligamentum flavum in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. J Orthop Res 2019;37:737–43. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MI, Attal N, Backonja MM, Baron R, Bouhassira D, Freynhagen R, Scholz J, Tölle TR, Wittchen H-U, Jensen TS. Using screening tools to identify neuropathic pain. PAIN 2007;127:199–203. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

