Performance of radiomics-based artificial intelligence systems in the diagnosis and prediction of treatment response and survival in esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy
- PMID: 37236811
- PMCID: PMC10789236
- DOI: 10.1093/dote/doad034
Performance of radiomics-based artificial intelligence systems in the diagnosis and prediction of treatment response and survival in esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy
Abstract
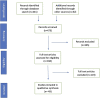
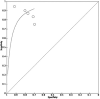
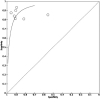
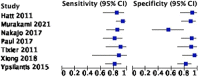
Radiomics can interpret radiological images with more detail and in less time compared to the human eye. Some challenges in managing esophageal cancer can be addressed by incorporating radiomics into image interpretation, treatment planning, and predicting response and survival. This systematic review and meta-analysis provides a summary of the evidence of radiomics in esophageal cancer. The systematic review was carried out using Pubmed, MEDLINE, and Ovid EMBASE databases-articles describing radiomics in esophageal cancer were included. A meta-analysis was also performed; 50 studies were included. For the assessment of treatment response using 18F-FDG PET/computed tomography (CT) scans, seven studies (443 patients) were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity and specificity were 86.5% (81.1-90.6) and 87.1% (78.0-92.8). For the assessment of treatment response using CT scans, five studies (625 patients) were included in the meta-analysis, with a pooled sensitivity and specificity of 86.7% (81.4-90.7) and 76.1% (69.9-81.4). The remaining 37 studies formed the qualitative review, discussing radiomics in diagnosis, radiotherapy planning, and survival prediction. This review explores the wide-ranging possibilities of radiomics in esophageal cancer management. The sensitivities of 18F-FDG PET/CT scans and CT scans are comparable, but 18F-FDG PET/CT scans have improved specificity for AI-based prediction of treatment response. Models integrating clinical and radiomic features facilitate diagnosis and survival prediction. More research is required into comparing models and conducting large-scale studies to build a robust evidence base.
Keywords: esophageal cancers; radiology; robotics.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of International Society for Diseases of the Esophagus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of distant interval metastases after neoadjuvant therapy for esophageal cancer with 18F-FDG PET(/CT): a systematic review and meta-analysis.Dis Esophagus. 2018 Dec 1;31(12). doi: 10.1093/dote/doy055. Dis Esophagus. 2018. PMID: 29917073
-
Radiomics diagnostic performance for predicting lymph node metastasis in esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Jun 12;24(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01278-5. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38867143 Free PMC article.
-
Interchangeability of radiomic features between [18F]-FDG PET/CT and [18F]-FDG PET/MR.Med Phys. 2019 Apr;46(4):1677-1685. doi: 10.1002/mp.13422. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 30714158
-
Radiomics for the Prediction of Treatment Outcome and Survival in Patients With Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2021 Mar;20(1):52-71. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2020.11.001. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33349519
-
Impact of [18F]FDG PET/CT Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Decision Making in Lung Cancer: Its Current Role.Semin Nucl Med. 2025 Mar;55(2):156-166. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2025.02.006. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Semin Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40050131 Review.
Cited by
-
18F-FDG PET/CT-based deep radiomic models for enhancing chemotherapy response prediction in breast cancer.Med Oncol. 2025 Aug 11;42(9):425. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02982-0. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40790010 Free PMC article.
-
Research status and progress of deep learning in automatic esophageal cancer detection.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 May 15;17(5):104410. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104410. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40487951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PSMA PET/CT for prostate cancer diagnosis: current applications and future directions.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 May 4;151(5):155. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06184-z. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40319443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Explanation and Elaboration with Examples for METRICS (METRICS-E3): an initiative from the EuSoMII Radiomics Auditing Group.Insights Imaging. 2025 Aug 13;16(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s13244-025-02061-y. Insights Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40802002 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics-clinical nomogram for preoperative lymph node metastasis prediction in esophageal carcinoma.Br J Radiol. 2024 Feb 28;97(1155):652-659. doi: 10.1093/bjr/tqae009. Br J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38268475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tourassi G D. Journey toward computer-aided diagnosis: role of image texture analysis. Radiology 1999; 213(2): 317–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

