Genome-wide association study of lung adenocarcinoma in East Asia and comparison with a European population
- PMID: 37236969
- PMCID: PMC10220065
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-38196-z
Genome-wide association study of lung adenocarcinoma in East Asia and comparison with a European population
Abstract
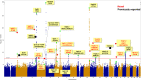
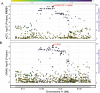
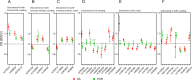
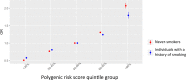
Lung adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer. Known risk variants explain only a small fraction of lung adenocarcinoma heritability. Here, we conducted a two-stage genome-wide association study of lung adenocarcinoma of East Asian ancestry (21,658 cases and 150,676 controls; 54.5% never-smokers) and identified 12 novel susceptibility variants, bringing the total number to 28 at 25 independent loci. Transcriptome-wide association analyses together with colocalization studies using a Taiwanese lung expression quantitative trait loci dataset (n = 115) identified novel candidate genes, including FADS1 at 11q12 and ELF5 at 11p13. In a multi-ancestry meta-analysis of East Asian and European studies, four loci were identified at 2p11, 4q32, 16q23, and 18q12. At the same time, most of our findings in East Asian populations showed no evidence of association in European populations. In our studies drawn from East Asian populations, a polygenic risk score based on the 25 loci had a stronger association in never-smokers vs. individuals with a history of smoking (Pinteraction = 0.0058). These findings provide new insights into the etiology of lung adenocarcinoma in individuals from East Asian populations, which could be important in developing translational applications.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U19 CA148127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025512/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA063673/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025522/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025476/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA231141/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA076292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121210/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025515/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 RC037004/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025514/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA167462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010480/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA203654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025511/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN045165/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA209414/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA077118/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA167462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 25514/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International

