Deep ultraviolet fluorescence microscopy of three-dimensional structures in the mouse brain
- PMID: 37237102
- PMCID: PMC10219975
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-35650-2
Deep ultraviolet fluorescence microscopy of three-dimensional structures in the mouse brain
Abstract
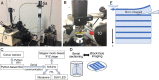
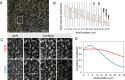
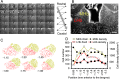
Three-dimensional (3D) imaging at cellular resolution improves our understanding of the brain architecture and is crucial for structural and functional integration as well as for the understanding of normal and pathological conditions in the brain. We developed a wide-field fluorescent microscope for 3D imaging of the brain structures using deep ultraviolet (DUV) light. This microscope allowed fluorescence imaging with optical sectioning due to the large absorption at the surface of the tissue and hence low tissue penetration of DUV light. Multiple channels of fluorophore signals were detected using single or a combination of dyes emitting fluorescence in the visible range of spectrum upon DUV excitation. Combination of this DUV microscope with microcontroller-based motorized stage enabled wide-field imaging of a coronal section of the cerebral hemisphere in mouse for deciphering cytoarchitecture of each substructure in detail. We extended this by integrating vibrating microtome which allowed serial block-face imaging of the brain structure such as the habenula in mouse. Acquired images were with resolution high enough for quantification of the cell numbers and density in the mouse habenula. Upon block-face imaging of the tissues covering entire extent of the cerebral hemisphere of the mouse brain, acquired data were registered and segmented for quantification of cell number in each brain regions. Results in the current analysis indicated that this novel microscope could be a convenient tool for large-scale 3D analysis of the brain in mice.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A workflow for 3D-CLEM investigating liver tissue.J Microsc. 2021 Mar;281(3):231-242. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12967. Epub 2020 Oct 27. J Microsc. 2021. PMID: 33034376
-
Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen with Deep-Red Emission for Through-Skull Three-Photon Fluorescence Imaging of Mouse.ACS Nano. 2017 Oct 24;11(10):10452-10461. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b05645. Epub 2017 Oct 12. ACS Nano. 2017. PMID: 29016105
-
3D cryo-imaging: a very high-resolution view of the whole mouse.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2009 Mar;292(3):342-51. doi: 10.1002/ar.20849. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2009. PMID: 19248166 Free PMC article.
-
Innovations in ex vivo Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2022 Jan;168:37-51. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2021.07.002. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34293338 Review.
-
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy: a review.J Histochem Cytochem. 2011 Feb;59(2):129-38. doi: 10.1369/0022155410394857. J Histochem Cytochem. 2011. PMID: 21339178 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NerveTracker: a Python-based software toolkit for visualizing and tracking groups of nerve fibers in serial block-face microscopy with ultraviolet surface excitation images.J Biomed Opt. 2024 Jul;29(7):076501. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.29.7.076501. Epub 2024 Jun 18. J Biomed Opt. 2024. PMID: 38912214 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

