Monthly mini-dose rituximab for primary anti-PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy: a personalized approach
- PMID: 37237260
- PMCID: PMC10213597
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-023-03206-1
Monthly mini-dose rituximab for primary anti-PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy: a personalized approach
Abstract
Background: The currently recommended dose of rituximab for primary membranous nephropathy is as high as that for lymphoma. However, the clinical manifestations of membranous nephropathy vary widely. Therefore, achieving individualized treatment is a topic that needs to be explored. This study assessed the efficacy of monthly mini-dose rituximab monotherapy in patients with primary membranous nephropathy.
Methods: This retrospective study included 32 patients with primary membranous nephropathy treated at Peking University Third Hospital between March 2019 and January 2023. All patients were anti-phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) antibody-positive and received rituximab 100 mg intravenously monthly for at least 3 months without other immunosuppressive therapy. Rituximab infusions were sustained until either remission of the nephrotic syndrome or a minimum serum anti-PLA2R titer ˂ 2 RU/mL was achieved.
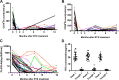
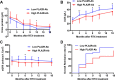
Results: The baseline parameters included: proteinuria, 8.5 ± 3.6 g/day; serum albumin, 24.8 ± 3.4 g/L; and anti-PLA2R antibody, 160 (20-2659) RU/mL. B-cell depletion was achieved in 87.5% patients after the first dose of rituximab 100 mg and in 100% after the second equivalent dose. The median follow-up was 24 months (range 18-38). Twenty-seven (84%) patients achieved remission, with 11 (34%) patients achieving complete remission by last follow-up. The relapse-free survival from the last infusion was 13.5 months (range 3-27). Patients were stratified into the low-titer (< 150 RU/mL, n = 17) and high-titer groups (≥ 150 RU/mL, n = 15) based on the anti-PLA2R titer. Sex, age, urinary proteins, serum albumin, and estimated glomerular filtration rate at baseline did not differ significantly between the two groups. At 18 months, compared to the low-titer group, the rituximab dose (960 ± 387 vs 694 ± 270 mg, p = 0.030) was higher, while serum albumin (37.0 ± 5.4 vs 41.3 ± 5.4 g/L, p = 0.033) and the complete remission rate (13% vs 53%, p = 0.000) were both lower in the high-titer group.
Conclusions: Monthly rituximab 100 mg appeared as a potential effective regimen for treating anti-PLA2R-associated primary membranous nephropathy with a low anti-PLA2R titer. The lower the anti-PLA2R titer, the lower the rituximab dose required to achieve remission.
Trial registration: A retrospective study, registered at ChiCTR (ChiCTR2200057381) on March 10, 2022.
Keywords: Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody; Membranous nephropathy; Mini-dose; Nephrotic syndrome; Rituximab.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Phospholipase A2 Receptor Antibody Titer Predicts Post-Rituximab Outcome of Membranous Nephropathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Oct;26(10):2545-58. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014070640. Epub 2015 Mar 24. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25804280 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Rituximab, Low-Dose Cyclophosphamide, and Prednisone for Primary Membranous Nephropathy: A Case Series With Extended Follow Up.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Dec;78(6):793-803. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.04.014. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 34174365
-
Effect of rituximab in patients with PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy and malignancy.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Jan 5;126:111327. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111327. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38056198
-
Treatment of rituximab in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a case series and literature review.Korean J Intern Med. 2022 Jul;37(4):830-840. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2021.155. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Korean J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35421909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of efficacy of rituximab for membranous nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 studies.Nephrol Ther. 2022 Apr;18(2):104-112. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2021.10.002. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Nephrol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35074299
Cited by
-
Case Report: Subcutaneous ofatumumab for patients with immunosuppressant-dependent or ineffective primary membranous nephropathy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 30;16:1610530. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1610530. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40661953 Free PMC article.
-
Dosing optimization of rituximab for primary membranous nephropathy by population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 26;15:1197651. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1197651. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38595918 Free PMC article.
-
Different Dosage Regimens of Rituximab in Primary Membranous Nephropathy Treatment: A Systematic Review.Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2024 Oct 29;17:265-273. doi: 10.2147/IJNRD.S489455. eCollection 2024. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 39493295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overlap of Primary Membranous Nephropathy, IgA Nephropathy, and Diabetic Nephropathy: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Nov 28;15(11):e49598. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49598. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38161828 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence-based personalised rituximab treatment protocol in membranous nephropathy (iRITUX): protocol for a multicentre randomised control trial.BMJ Open. 2025 Apr 2;15(4):e093920. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093920. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40180405 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

