Histone lysine methyltransferase SMYD3 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis via H3K4me3-mediated HMGA2 transcription
- PMID: 37237385
- PMCID: PMC10223939
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-023-01506-9
Histone lysine methyltransferase SMYD3 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis via H3K4me3-mediated HMGA2 transcription
Abstract
Background: Epigenetic dysregulation is essential to the tumorigenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). SET and MYND domain-containing protein 3 (SMYD3), a histone lysine methyltransferase, is implicated in gene transcription regulation and tumor development. However, the roles of SMYD3 in OSCC initiation are not fully understood. The present study investigated the biological functions and mechanisms involved in the SMYD3-mediated tumorigenesis of OSCC utilizing bioinformatic approaches and validation assays with the aim of informing the development of targeted therapies for OSCC.
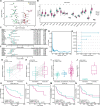
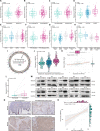
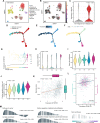
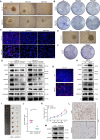
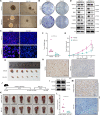
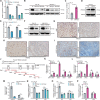
Results: 429 chromatin regulators were screened by a machine learning approach and aberrant expression of SMYD3 was found to be closely associated with OSCC formation and poor prognosis. Data profiling of single-cell and tissue demonstrated that upregulated SMYD3 significantly correlated with aggressive clinicopathological features of OSCC. Alterations in copy number and DNA methylation patterns may contribute to SMYD3 overexpression. Functional experimental results suggested that SMYD3 enhanced cancer cell stemness and proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. SMYD3 was observed to bind to the High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2 (HMGA2) promoter and elevated tri-methylation of histone H3 lysine 4 at the corresponding site was responsible for transactivating HMGA2. SMYD3 also was positively linked to HMGA2 expression in OSCC samples. Furthermore, treatment with the SMYD3 chemical inhibitor BCI-121 exerted anti-tumor effects.
Conclusions: Histone methyltransferase activity and transcription-potentiating function of SMYD3 were found to be essential for tumorigenesis and the SMYD3-HMGA2 is a potential therapeutic target in OSCC.
Keywords: Epigenetics; HMGA2; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; SMYD3; Tumorigenesis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yang Z, Yan G, Zheng L, Gu W, Liu F, Chen W, et al. YKT6, as a potential predictor of prognosis and immunotherapy response for oral squamous cell carcinoma, is related to cell invasion, metastasis, and CD8+ T cell infiltration. Oncoimmunology. 2021;10:1938890. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1938890. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

