Isolation of Biologically Active Compounds from Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences by Using Different Extraction Solvents and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity
- PMID: 37237864
- PMCID: PMC10215227
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12050998
Isolation of Biologically Active Compounds from Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences by Using Different Extraction Solvents and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
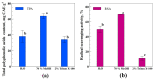
Hemp inflorescences are a source of vital compounds, including phytocannabinoids and other biologically active compounds. Various methods are adapted for the extraction of these vital compounds such as the use of different organic solvents. This study aimed to assess the comparative extraction potential of three different solvents: deionized water, 70% methanol (MeOH), and 2% Triton X-100, for phytochemicals in hemp inflorescences. Spectrophotometric techniques were applied to investigate the total amount of polyphenolic compounds (TPC), total flavonoids contents (TF), phenolic acids (TPA), and radical scavenging activity (RSA) in hemp extracts obtained using different polarity solvents. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry was used for cannabinoids and organic acids quantitative analysis. In the results, MeOH showed a better affinity for the recovery of TFC, TPA, and RSA in comparison to Triton X-100 and water. However, Triton X-100 performed better for TPC with 4-folds and 33% turnover compared to water and MeOH, respectively. Six cannabinoids (CBDVA, CBL, CBD, CBC, CBN, and CBG) were identified in hemp inflorescence extracts. The maximum determined concentration was as follows: CBD > CBC > CBG > CBDVA > CBL > CBN. Overall, fourteen organic acids were identified. Hemp inflorescence extracts obtained using 2% Triton X-100 showed an effect on all tested strains of microorganisms. Methanolic and aqueous extracts had antimicrobial activity against seven tested strains. On the other hand, the inhibition zones were wider for methanolic extracts compared to aqueous ones. Hemp aqua extract with antimicrobial activity might be used in various markets where toxic solvents are unwanted.
Keywords: CBD; Cannabis sativa L.; antimicrobial activity; polyphenolic compounds; radical scavenging activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Šain A., Matešić N., Jurina T., Jurinjak Tušek A., Benković M., Valinger D., Gajdoš Kljusurić J. Optimization of ethanol/water solvent extraction of bioactive components originating from industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Hrana u Zdravlju i Bolesti: Znanstveno-Stručni časopis za Nutricionizam i Dijetetiku. 2020;9:30–39.
-
- Baldini M., Ferfuia C., Piani B., Sepulcri A., Dorigo G., Zuliani F., Danuso F., Cattivello C. The Performance and Potentiality of Monoecious Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivars as a Multipurpose Crop. Agronomy. 2018;8:162. doi: 10.3390/agronomy8090162. - DOI
-
- Barčauskaitė K., Žydelis R., Ruzgas R., Bakšinskaitė A., Tilvikienė V. The Seeds of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis Sativa L.) a Source of Minerals and Biologically Active Compounds. J. Nat. Fibers. 2022;19:13025–13039. doi: 10.1080/15440478.2022.2084486. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

