Human Sperm as an In Vitro Model to Assess the Efficacy of Antioxidant Supplements during Sperm Handling: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 37237965
- PMCID: PMC10215929
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12051098
Human Sperm as an In Vitro Model to Assess the Efficacy of Antioxidant Supplements during Sperm Handling: A Narrative Review
Abstract
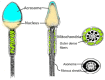
Spermatozoa are highly differentiated cells that produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) due to aerobic metabolism. Below a certain threshold, ROS are important in signal transduction pathways and cellular physiological processes, whereas ROS overproduction damages spermatozoa. Sperm manipulation and preparation protocols during assisted reproductive procedures-for example, cryopreservation-can result in excessive ROS production, exposing these cells to oxidative damage. Thus, antioxidants are a relevant topic in sperm quality. This narrative review focuses on human spermatozoa as an in vitro model to study which antioxidants can be used to supplement media. The review comprises a brief presentation of the human sperm structure, a general overview of the main items of reduction-oxidation homeostasis and the ambivalent relationship between spermatozoa and ROS. The main body of the paper deals with studies in which human sperm have been used as an in vitro model to test antioxidant compounds, including natural extracts. The presence and the synergic effects of different antioxidant molecules could potentially lead to more effective products in vitro and, in the future, in vivo.
Keywords: antioxidants; human sperm in vitro; natural extract; oxidative stress; pathological role of ROS; physiological role of ROS; phytocomplexes; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen. 6th ed. WHO Press; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021.
-
- Leslie S.W., Soon-Sutton T.L., Khan M.A.B. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. Male infertility. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

