Different BD BACTEC™ Blood Culture Bottle Types for the Detection of Fungi in Simulated Sterile Body Fluid Samples
- PMID: 37238183
- PMCID: PMC10217702
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13101699
Different BD BACTEC™ Blood Culture Bottle Types for the Detection of Fungi in Simulated Sterile Body Fluid Samples
Abstract
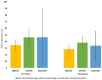
Blood culture systems are a potential alternative to classical cultivation of fungi on mycological media, but there are limited data on the suitability of these systems for culturing other sample types (e.g., sterile body fluids). We conducted a prospective study to evaluate different types of blood culture (BC) bottles for the detection of different fungal species in non-blood samples. A total of 43 fungal isolates were tested for their ability to grow in BD BACTEC Mycosis-IC/F (Mycosis bottles), BD BACTEC Plus Aerobic/F (Aerobic bottles) and BD BACTEC Plus Anaerobic/F (Anaerobic bottles) (Becton Dickinson, East Rutherford, NJ, USA) BC bottles inoculated with spiked samples without the addition of blood or fastidious organism supplement. Time to detection (TTD) was determined for all BC types tested and compared between groups. In general, Mycosis and Aerobic bottles were similar (p > 0.05). The Anaerobic bottles failed to support growth in >86% of cases. The Mycosis bottles were superior in detecting Candida glabrata, Cryptococcus spp. and Aspergillus spp. (p < 0.05). The performance of Mycosis and Aerobic bottles was similar, but if cryptococcosis or aspergillosis is suspected, the use of Mycosis bottles is recommended. Anaerobic bottles are not recommended for fungal detection.
Keywords: Aspergillus; BD BACTEC Mycosis-IC/F; BD BACTEC Plus Aerobic/F; Candida; Cryptococcus; blood cultures; fungal infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gangneux J.P., Bougnoux M.E., Hennequin C., Godet C., Chandenier J., Denning D., Dupont B., LIFE program, the Société Française de Mycologie Médicale SFMM-Study Group An estimation of burden of serious fungal infections in France. J. Mycol. Med. 2016;26:385–390. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2016.11.001. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous