A Bibliometric Analysis on Arrhythmia Detection and Classification from 2005 to 2022
- PMID: 37238216
- PMCID: PMC10217318
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13101732
A Bibliometric Analysis on Arrhythmia Detection and Classification from 2005 to 2022
Abstract
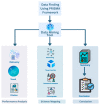
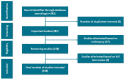
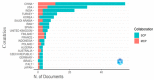
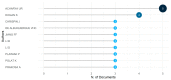
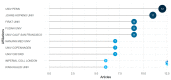
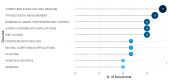
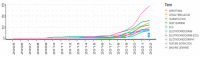
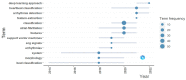
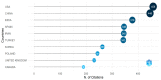
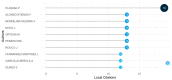
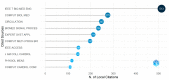
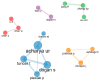
Bibliometric analysis is a widely used technique for analyzing large quantities of academic literature and evaluating its impact in a particular academic field. In this paper bibliometric analysis has been used to analyze the academic research on arrhythmia detection and classification from 2005 to 2022. We have followed PRISMA 2020 framework to identify, filter and select the relevant papers. This study has used the Web of Science database to find related publications on arrhythmia detection and classification. "Arrhythmia detection", "arrhythmia classification" and "arrhythmia detection and classification" are three keywords for gathering the relevant articles. 238 publications in total were selected for this research. In this study, two different bibliometric techniques, "performance analysis" and "science mapping", were applied. Different bibliometric parameters such as publication analysis, trend analysis, citation analysis, and networking analysis have been used to evaluate the performance of these articles. According to this analysis, the three countries with the highest number of publications and citations are China, the USA, and India in terms of arrhythmia detection and classification. The three most significant researchers in this field are those named U. R. Acharya, S. Dogan, and P. Plawiak. Machine learning, ECG, and deep learning are the three most frequently used keywords. A further finding of the study indicates that the popular topics for arrhythmia identification are machine learning, ECG, and atrial fibrillation. This research provides insight into the origins, current status, and future direction of arrhythmia detection research.
Keywords: PRISMA; arrhythmia detection; bibliometric analysis; biblioshiny.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


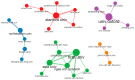
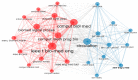
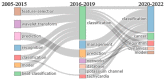
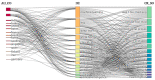
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

