Electrochemical Creatinine (Bio)Sensors for Point-of-Care Diagnosis of Renal Malfunction and Chronic Kidney Disorders
- PMID: 37238220
- PMCID: PMC10217452
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13101737
Electrochemical Creatinine (Bio)Sensors for Point-of-Care Diagnosis of Renal Malfunction and Chronic Kidney Disorders
Abstract
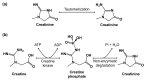
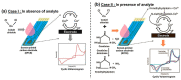
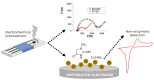
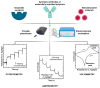
In the post-pandemic era, point-of-care (POC) diagnosis of diseases is an important research frontier. Modern portable electrochemical (bio)sensors enable the design of POC diagnostics for the identification of diseases and regular healthcare monitoring. Herein, we present a critical review of the electrochemical creatinine (bio)sensors. These sensors either make use of biological receptors such as enzymes or employ synthetic responsive materials, which provide a sensitive interface for creatinine-specific interactions. The characteristics of different receptors and electrochemical devices are discussed, along with their limitations. The major challenges in the development of affordable and deliverable creatinine diagnostics and the drawbacks of enzymatic and enzymeless electrochemical biosensors are elaborated, especially considering their analytical performance parameters. These revolutionary devices have potential biomedical applications ranging from early POC diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and other kidney-related illnesses to routine monitoring of creatinine in elderly and at-risk humans.
Keywords: biosensors; creatinine; diagnostics; kidney failure; point-of-care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modern creatinine (Bio)sensing: Challenges of point-of-care platforms.Biosens Bioelectron. 2019 Apr 1;130:110-124. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.048. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019. PMID: 30731344 Review.
-
Miniaturized Bio-and Chemical-Sensors for Point-of-Care Monitoring of Chronic Kidney Diseases.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Mar 22;18(4):942. doi: 10.3390/s18040942. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29565315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2D Materials in Development of Electrochemical Point-of-Care Cancer Screening Devices.Micromachines (Basel). 2019 Sep 30;10(10):662. doi: 10.3390/mi10100662. Micromachines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31575012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical creatinine detection for advanced point-of-care sensing devices: a review.RSC Adv. 2022 Oct 27;12(47):30785-30802. doi: 10.1039/d2ra04479j. eCollection 2022 Oct 24. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36349154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-based electrochemical biosensors: an alternative for point-of-care diagnostics?Talanta. 2024 Oct 1;278:126467. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.126467. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Talanta. 2024. PMID: 38968657 Review.
Cited by
-
Core-shell niobium(v) oxide@molecularly imprinted polythiophene nanoreceptors for transformative, real-time creatinine analysis.Nanoscale Adv. 2024 May 31;6(14):3644-3654. doi: 10.1039/d4na00300d. eCollection 2024 Jul 9. Nanoscale Adv. 2024. PMID: 38989513 Free PMC article.
-
The Versatility of Biological Field-Effect Transistor-Based Biosensors (BioFETs) in Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Applications and Future Directions for Peritoneal Dialysis Monitoring.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;15(3):193. doi: 10.3390/bios15030193. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using a Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Device with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for the Quantification of Tartrazine in Soda Drinks.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;13(6):639. doi: 10.3390/bios13060639. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37367004 Free PMC article.
-
Label-Free, Impedance-Based Biosensor for Kidney Disease Biomarker Uromodulin.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Dec 8;23(24):9696. doi: 10.3390/s23249696. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139542 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile health management among end stage renal disease patients: a scoping review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 11;11:1366362. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1366362. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39055692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pundir C.S., Yadav S., Kumar A. Creatinine sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013;50:42–52. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2013.04.013. - DOI
-
- Ceriotti F., Boyd J.C., Klein G., Henny J., Queraltó J., Kairisto V., Panteghini M., the IFCC Committee on Reference Intervals and Decision Limits (C-RIDL) Reference Intervals for Serum Creatinine Concentrations: Assessment of Available Data for Global Application. Clin. Chem. 2008;54:559–566. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2007.099648. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

