Medical Imaging of Inflammations and Infections of Breast Implants
- PMID: 37238291
- PMCID: PMC10217528
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13101807
Medical Imaging of Inflammations and Infections of Breast Implants
Abstract
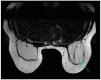
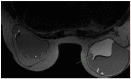
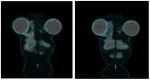
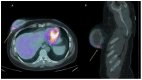
Breast implants are widely used for reconstructive and/or cosmetic purposes. Inflammations and infections of breast implants represent important complications in clinical practice. The proper management of complications is necessary: diagnostic imaging plays a key role in detecting sites of inflammation and/or infection. The present review aims to illustrate the radiological findings of these conditions with different imaging techniques, such as mammography (MX), ultrasound (US), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and nuclear medicine imaging. A knowledge of these findings is essential for radiologists and nuclear medicine physicians to provide helpful information for the clinical management of these complications.
Keywords: breast implant infections; magnetic resonance imaging; mammography; positron emission tomography; scintigraphy; ultrasound imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stefura T., Rusinek J., Wątor J., Zagórski A., Zając M., Libondi G., Wysocki W.M., Koziej M. Implant vs. autologous tissue-based breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the studies comparing surgical approaches in 55,455 patients. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023;77:346–358. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2022.11.044. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) 2018 Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. 2018. [(accessed on 1 March 2023)]. Available online: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2018/plastic-su....
-
- Saldanha I.J., Broyles J.M., Adam G.P., Cao W., Bhuma M.R., Mehta S., Pusic A.L., Dominici L.S., Balk E.M. Implant-based Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2022;10:e4179. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004179. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

