Asymptotic Distribution of Certain Types of Entropy under the Multinomial Law
- PMID: 37238489
- PMCID: PMC10217615
- DOI: 10.3390/e25050734
Asymptotic Distribution of Certain Types of Entropy under the Multinomial Law
Abstract
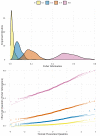
We obtain expressions for the asymptotic distributions of the Rényi and Tsallis of order q entropies and Fisher information when computed on the maximum likelihood estimator of probabilities from multinomial random samples. We verify that these asymptotic models, two of which (Tsallis and Fisher) are normal, describe well a variety of simulated data. In addition, we obtain test statistics for comparing (possibly different types of) entropies from two samples without requiring the same number of categories. Finally, we apply these tests to social survey data and verify that the results are consistent but more general than those obtained with a χ2 test.
Keywords: asymptotic distributions; entropy; hypothesis tests; multinomial distribution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson N.L., Kotz S., Balakrishnan N. Discrete Multivariate Distributions. Wiley-Interscience; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 1997.
-
- Modis T. Links between entropy, complexity, and the technological singularity. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022;176:121457. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121457. - DOI
-
- Hutcheson K., Shenton L.R. Some moments of an estimate of Shannon’s measure of information. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods. 1974;3:89–94. doi: 10.1080/03610927408827106. - DOI
-
- Jacquet P., Szpankowski W. Entropy computations via analytic depoissonization. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 1999;45:1072–1081. doi: 10.1109/18.761251. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

