Comparison of the Penetration Depth of 905 nm and 1064 nm Laser Light in Surface Layers of Biological Tissue Ex Vivo
- PMID: 37239026
- PMCID: PMC10216207
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11051355
Comparison of the Penetration Depth of 905 nm and 1064 nm Laser Light in Surface Layers of Biological Tissue Ex Vivo
Abstract
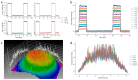
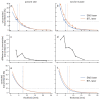
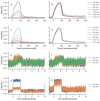
The choice of parameters for laser beams used in the treatment of musculoskeletal diseases is of great importance. First, to reach high penetration depths into biological tissue and, secondly, to achieve the required effects on a molecular level. The penetration depth depends on the wavelength since there are multiple light-absorbing and scattering molecules in tissue with different absorption spectra. The present study is the first comparing the penetration depth of 1064 nm laser light with light of a smaller wavelength (905 nm) using high-fidelity laser measurement technology. Penetration depths in two types of tissue ex vivo (porcine skin and bovine muscle) were investigated. The transmittance of 1064 nm light through both tissue types was consistently higher than of 905 nm light. The largest differences (up to 5.9%) were seen in the upper 10 mm of tissue, while the difference vanished with increasing tissue thickness. Overall, the differences in penetration depth were comparably small. These results may be of relevance in the selection of a certain wavelength in the treatment of musculoskeletal diseases with laser therapy.
Keywords: 1064 nm NIR laser; 905 nm NIR laser; continuous wave lasers; laser therapy; musculoskeletal system; porcine/bovine tissues; pulsed lasers; tissue penetration depth.
Conflict of interest statement
Up until December 2017, C.S. served as a consultant for Electro Medical Systems (Nyon, Switzerland), and has received funding from Electro Medical Systems for conducting basic research on radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy and laser therapy at his lab. Regarding the present study, Electro Medical Systems did not impose any constraints on publication of the data and had no role in the design of the study; in data collection, analyses, or interpretation; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the findings.
Figures


References
-
- Naterstad I.F., Joensen J., Bjordal J.M., Couppé C., Lopes-Martins R.A.B., Stausholm M.B. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy in patients with lower extremity tendinopathy or plantar fasciitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e059479. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059479. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bjordal J.M., Lopes-Martins R.A.B., Joensen J., Iversen V.V. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of low level laser therapy and its relevance for clinical use in physiotherapy. Phys. Ther. Rev. 2010;15:286–293. doi: 10.1179/1743288X10Y.0000000001. - DOI
-
- Schmitz C. Improving extracorporeal shock wave therapy with 904 or 905 nm pulsed, high power laser pretreatment. Preprints. 2021:2021010138. doi: 10.20944/preprints202101.0138.v1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

