Osteopontin in Pulmonary Hypertension
- PMID: 37239056
- PMCID: PMC10216394
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11051385
Osteopontin in Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a pathological condition with multifactorial etiology, which is characterized by elevated pulmonary arterial pressure and pulmonary vascular remodeling. The underlying pathogenetic mechanisms remain poorly understood. Accumulating clinical evidence suggests that circulating osteopontin may serve as a biomarker of PH progression, severity, and prognosis, as well as an indicator of maladaptive right ventricular remodeling and dysfunction. Moreover, preclinical studies in rodent models have implicated osteopontin in PH pathogenesis. Osteopontin modulates a plethora of cellular processes within the pulmonary vasculature, including cell proliferation, migration, apoptosis, extracellular matrix synthesis, and inflammation via binding to various receptors such as integrins and CD44. In this article, we provide a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of osteopontin regulation and its impact on pulmonary vascular remodeling, as well as consider research issues required for the development of therapeutics targeting osteopontin as a potential strategy for the management of PH.
Keywords: biomarkers; osteopontin; pulmonary hypertension; right heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

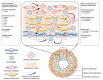

 —indicates that animal models with the corresponding osteopontin manipulations are available; NA—studies with the corresponding animal models and osteopontin manipulations are not available. (B) No experimental studies have evaluated effects of recombinant osteopontin application or osteopontin-neutralizing antibodies. In order to elucidate the cell specific roles of osteopontin, the Cre/LoxP system can be utilized using cell-specific promoter systems. Further, to better characterize the role of osteopontin in such models it is recommended to use invasive catheterization (C) to measure right atrial (RA) pressure, right ventricular (RV) systolic pressure (RVSP), RV diastolic pressure (RVDP), aortic pressure, left ventricular (LV) systolic pressure (LVSP) and LV diastolic pressure (LVDP). Echocardiographic imaging (D) of the heart is also warranted to inform additional characteristics of the RV including both systolic and diastolic functions, including the following parameters: the ratio of pulmonary artery acceleration time to pulmonary artery ejection time (PAAT/PAET), tricuspid annulus systolic excursion (TAPSE), RV annulus systolic velocity (RV-S´), RV internal diameter (RVID), RV wall thickness (RVWT), stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), LV eccentricity index (LVEI), tricuspid valve inflow velocities (TV E/A), and tricuspid annulus lateral velocities (TV E´/A´). Following the terminal catheterization and echocardiography assessments, lung and heart tissues (E) can be evaluated ex vivo for pulmonary artery (PA) wall thickness, muscularization and inflammation, as well as lung capillary density. RV tissue can be assessed for RV fibrosis, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Furthermore, lung and RV tissues can be studied for the expression of genes and proteins involved in various pathological processes including inflammation, extracellular matrix (ECM) synthesis and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT). Finally, the exact cellular roles of osteopontin can be studied in vitro (F) using cell culture techniques under both osteopontin loss- and gain-of-function conditions to assess cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. Employing such strategies in rodent pulmonary hypertension models, and ex vivo tissue and in vitro cell culture experiments may be necessary to fully characterize the role of osteopontin in pulmonary hypertension.
—indicates that animal models with the corresponding osteopontin manipulations are available; NA—studies with the corresponding animal models and osteopontin manipulations are not available. (B) No experimental studies have evaluated effects of recombinant osteopontin application or osteopontin-neutralizing antibodies. In order to elucidate the cell specific roles of osteopontin, the Cre/LoxP system can be utilized using cell-specific promoter systems. Further, to better characterize the role of osteopontin in such models it is recommended to use invasive catheterization (C) to measure right atrial (RA) pressure, right ventricular (RV) systolic pressure (RVSP), RV diastolic pressure (RVDP), aortic pressure, left ventricular (LV) systolic pressure (LVSP) and LV diastolic pressure (LVDP). Echocardiographic imaging (D) of the heart is also warranted to inform additional characteristics of the RV including both systolic and diastolic functions, including the following parameters: the ratio of pulmonary artery acceleration time to pulmonary artery ejection time (PAAT/PAET), tricuspid annulus systolic excursion (TAPSE), RV annulus systolic velocity (RV-S´), RV internal diameter (RVID), RV wall thickness (RVWT), stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), LV eccentricity index (LVEI), tricuspid valve inflow velocities (TV E/A), and tricuspid annulus lateral velocities (TV E´/A´). Following the terminal catheterization and echocardiography assessments, lung and heart tissues (E) can be evaluated ex vivo for pulmonary artery (PA) wall thickness, muscularization and inflammation, as well as lung capillary density. RV tissue can be assessed for RV fibrosis, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Furthermore, lung and RV tissues can be studied for the expression of genes and proteins involved in various pathological processes including inflammation, extracellular matrix (ECM) synthesis and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT). Finally, the exact cellular roles of osteopontin can be studied in vitro (F) using cell culture techniques under both osteopontin loss- and gain-of-function conditions to assess cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. Employing such strategies in rodent pulmonary hypertension models, and ex vivo tissue and in vitro cell culture experiments may be necessary to fully characterize the role of osteopontin in pulmonary hypertension.References
-
- Humbert M., Guignabert C., Bonnet S., Dorfmuller P., Klinger J.R., Nicolls M.R., Olschewski A.J., Pullamsetti S.S., Schermuly R.T., Stenmark K.R., et al. Pathology and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension: State of the art and research perspectives. Eur. Respir. J. 2019;53:1801887. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01887-2018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Humbert M., Kovacs G., Hoeper M.M., Badagliacca R., Berger R.M.F., Brida M., Carlsen J., Coats A.J.S., Escribano-Subias P., Ferrari P., et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2022;43:3618–3731. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac237. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

