RETRACTED: Sinapic Acid Attenuate Liver Injury by Modulating Antioxidant Activity and Inflammatory Cytokines in Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Cirrhosis in Rats
- PMID: 37239118
- PMCID: PMC10216417
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11051447
RETRACTED: Sinapic Acid Attenuate Liver Injury by Modulating Antioxidant Activity and Inflammatory Cytokines in Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Cirrhosis in Rats
Retraction in
-
RETRACTED: Jabbar et al. Sinapic Acid Attenuate Liver Injury by Modulating Antioxidant Activity and Inflammatory Cytokines in Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Cirrhosis in Rats. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1447.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 3;13(4):862. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040862. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40202769 Free PMC article.
Abstract
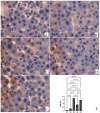
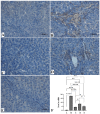
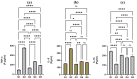
Sinapic acid (SA) is a natural pharmacological active compound found in berries, nuts, and cereals. The current study aimed to investigate the protective effects of SA against thioacetamide (TAA) fibrosis in rats by histopathological and immunohistochemical assays. The albino rats (30) were randomly divided into five groups (G). G1 was injected with distilled water 3 times/week and fed orally daily with 10% Tween 20 for two months. G2-5 were injected with 200 mg/kg TAA three times weekly for two months and fed with 10% Tween 20, 50 mg/kg silymarin, 20, and 40 mg/kg of SA daily for 2 months, respectively. The results showed that rats treated with SA had fewer hepatocyte injuries with lower liver index (serum bilirubin, total protein, albumin, and liver enzymes (ALP, ALT, and AST) and were similar to that of control and silymarin-treated rats. Acute toxicity for 2 and 4 g/kg SA showed to be safe without any toxic signs in treated rats. Macroscopic examination showed that hepatotoxic liver had an irregular, rough surface with micro and macro nodules and histopathology expressed by Hematoxylin and Eosin, and Masson Trichrome revealed severe inflammation and infiltration of focal necrosis, fibrosis, lymphocytes, and proliferation bile duct. In contrast, rats fed with SA had significantly lower TAA toxicity in gross and histology and liver tissues as presented by less liver tissue disruption, lesser fibrosis, and minimum in filtered hepatocytes. Immunohistochemistry of rats receiving SA showed significant up-regulation of HSP 70% and down-regulation of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) protein expression compared to positive control rats. The homogenized liver tissues showed a notable rise in the antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT) actions with significantly lower malondialdehyde (MDA) levels compared to that of the positive control group. Furthermore, the SA-treated rats had significantly lower TNF-a, IL-6, and higher IL-10 levels than the positive control rats. Thus, the findings suggest SA as a hepatoprotective compound due to its inhibitory effects on fibrosis, hepatotoxicity, liver cell proliferation, up-regulation of HSP 70, and downregulation of α-SMA expression, inhibiting lipid peroxidation (MDA), while retaining the liver index and antioxidant enzymes to normal.
Keywords: TAA; histology; immunohistochemistry; liver cirrhosis; sinapic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effect of pinostrobin against thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis in rats.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023 Jan;30(1):103506. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103506. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36458098 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of methanolic extract of green tea against Thioacetamide-Induced liver injury in Sprague Dawley rats.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan;29(1):564-573. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.023. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002452 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo hepatoprotective effect of Morinda elliptica stem extract against liver fibrosis induced by thioacetamide.Environ Toxicol. 2021 Dec;36(12):2404-2413. doi: 10.1002/tox.23353. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Environ Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34436826
-
Protective effects of shikimic acid against thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis: role of Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 30;16:1609711. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1609711. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40520202 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of Gynura procumbens against thioacetamide-induced cirrhosis in rats: Targeting inflammatory and oxidative stress signalling pathways.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 23;9(9):e19418. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19418. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37662795 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sinapic acid modulates oxidative stress and metabolic disturbances to attenuate ovarian fibrosis in letrozole-induced polycystic ovary syndrome SD rats.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Jan 24;12(4):2917-2931. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3973. eCollection 2024 Apr. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38628198 Free PMC article.
-
Sinomenine accelerate wound healing in rats by augmentation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunuhistochemical pathways.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 11;10(1):e23581. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23581. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38173533 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan nanoparticle encapsulation increased the prophylactic efficacy of Lactobacillus plantarum RM1 against AFM1-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Dec;30(59):123925-123938. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-31016-3. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37995030 Free PMC article.
-
A flavonoid Ombuin ameliorates thioacetamide-mediated liver cirrhosis in vivo: biochemical, immunohistochemical, inflammatory approaches.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 30. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04147-2. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40304746
-
RETRACTED: Jabbar et al. Sinapic Acid Attenuate Liver Injury by Modulating Antioxidant Activity and Inflammatory Cytokines in Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Cirrhosis in Rats. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1447.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 3;13(4):862. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040862. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40202769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Medhtiy M.H., Jabbar A.A., Shareef S.H., Ibrahim I.A.A., Alzahrani A.R., Abdulla M.A. Histopathological Evaluation of Annona muricata in TAA-Induced Liver Injury in Rats. Processes. 2022;10:1613. doi: 10.3390/pr10081613. - DOI
-
- da Silva B.S., Paulino A.M.B., Taffarel M., Borba I.G., Telles L.O., Lima V.V., Aguiar D.H., Dias M.C., Nascimento A.F., Sinhorin V.D.G., et al. High sucrose diet attenuates oxidative stress, inflammation and liver injury in thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis. Life Sci. 2021;267:118944. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118944. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

