Histologic Analysis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis by Morphometric and Fractal Analysis
- PMID: 37239155
- PMCID: PMC10216340
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11051483
Histologic Analysis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis by Morphometric and Fractal Analysis
Abstract
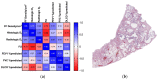
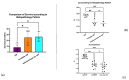
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive fibrotic lung disorder, ultimately leading to respiratory failure and death. Despite great research advances in understanding the mechanisms underlying the disease, its diagnosis, and its treatment, IPF still remains idiopathic without known biological or histological markers able to predict disease progression or response to treatment. The histologic hallmark of IPF is usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP), with its intricate architectural distortion and temporal inhomogeneity. We hypothesize that normal lung alveolar architecture can be compared to fractals, such as the Pythagoras tree with its fractal dimension (Df), and every pathological insult, distorting the normal lung structure, could result in Df variations. In this study, we aimed to assess the UIP histologic fractal dimension in relationship to other morphometric parameters in newly diagnosed IPF patients and its possible role in the prognostic stratification of the disease. Clinical data and lung tissue specimens were obtained from twelve patients with IPF, twelve patients with non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), and age-matched "healthy" control lung tissue from patients undergoing lung surgery for other causes. Histology and histomorphometry were performed to evaluate Df and lacunarity measures, using the box counting method on the FracLac ImageJ plugin. The results showed that Df was significantly higher in IPF patients compared to controls and fibrotic NSIP patients, indicating greater architectural distortion in IPF. Additionally, high Df values were associated with higher fibroblastic foci density and worse prognostic outcomes in IPF, suggesting that Df may serve as a potential novel prognostic marker for IPF. The scalability of Df measurements was demonstrated through repeated measurements on smaller portions from the same surgical biopsies, which were selected to mimic a cryobiopsy. Our study provides further evidence to support the use of fractal morphometry as a tool for quantifying and determining lung tissue remodeling in IPF, and we demonstrated a significant correlation between histological and radiological Df in UIP pattern, as well as a significant association between Df and FF density. Furthermore, our study demonstrates the scalability and self-similarity of Df measurements across different biopsy types, including surgical and smaller specimens.
Keywords: IPF; UIP; fractals; histomorphometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Raghu G., Remy-Jardin M., Richeldi L., Thomson C.C., Inoue Y., Johkoh T., Kreuter M., Lynch D.A., Maher T.M., Martinez F.J., et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022;205:e18–e47. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202202-0399ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keow J., Cecchini M.J., Jayawardena N., Zompatori M., Joseph M.G., Mura M. Digital Quantification of P16-Positive Foci in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease Is Associated with a Phenotype of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis with Reduced Survival. Respir. Res. 2022;23:147. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02067-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

