Reversal Training Discloses Gender Differences in a Spatial Memory Task in Humans
- PMID: 37239212
- PMCID: PMC10216308
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13050740
Reversal Training Discloses Gender Differences in a Spatial Memory Task in Humans
Abstract
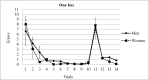
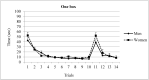
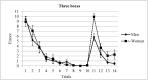
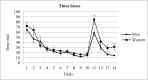
Over the past few years, spatial memory has been studied using virtual-reality-based tasks. Reversal learning has been widely used in spatial orientation tasks for testing, among other things, new learning and flexibility. By means of a reversal-learning protocol, we assessed spatial memory in men and women. A total of sixty participants (half of them women) performed a task that included two phases: during the acquisition phase, participants were asked to find one or three rewarded positions in the virtual room across ten trials. During the reversal phase, the rewarded boxes were moved to a new position and maintained for four trials. The results showed that men and women differed in the reversal phase, with men outperforming women in high demanding conditions. Dissimilarities in several cognitive abilities between both genders are the base of these differences and are discussed.
Keywords: dimorphism; flexibility; hippocampus; sex differences; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Virtual reality assessment of walking and non-walking space in men and women with virtual reality-based tasks.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 2;13(10):e0204995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204995. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30278083 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual orientation and spatial memory.Psicothema. 2011 Nov;23(4):752-8. Psicothema. 2011. PMID: 22047869
-
Almeria spatial memory recognition test (ASMRT): Gender differences emerged in a new passive spatial task.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Jun 9;651:188-191. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.05.011. Epub 2017 May 9. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28499888
-
Learning and metabolic brain differences between juvenile male and female rats in the execution of different training regimes of a spatial memory task.Physiol Behav. 2023 Aug 1;267:114203. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2023.114203. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Physiol Behav. 2023. PMID: 37086830 Review.
-
Spatial skills.Handb Clin Neurol. 2020;175:65-79. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64123-6.00006-0. Handb Clin Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33008544 Review.
Cited by
-
The Contribution of Internal and External Factors to Human Spatial Navigation.Brain Sci. 2024 Jun 7;14(6):585. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14060585. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928585 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

