Erectile Dysfunction: Treatments, Advances and New Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 37239274
- PMCID: PMC10216368
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13050802
Erectile Dysfunction: Treatments, Advances and New Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
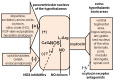
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to get and maintain an adequate penile erection for satisfactory sexual intercourse. Due to its negative impacts on men's life quality and increase during aging (40% of men between 40 and 70 years), ED has always attracted researchers of different disciplines, from urology, andrology and neuropharmacology to regenerative medicine, and vascular and prosthesis implant surgery. Locally and/or centrally acting drugs are used to treat ED, e.g., phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (first in the list) given orally, and phentolamine, prostaglandin E1 and papaverine injected intracavernously. Preclinical data also show that dopamine D4 receptor agonists, oxytocin and α-MSH analogues may have a role in ED treatment. However, since pro-erectile drugs are given on demand and are not always efficacious, new strategies are being tested for long lasting cures of ED. These include regenerative therapies, e.g., stem cells, plasma-enriched platelets and extracorporeal shock wave treatments to cure damaged erectile tissues. Although fascinating, these therapies are laborious, expensive and not easily reproducible. This leaves old vacuum erection devices and penile prostheses as the only way to get an artificial erection and sexual intercourse with intractable ED, with penile prosthesis used only by accurately selected patients.
Keywords: erectile dysfunction; penile prosthesis; pharmacological treatments; regenerative strategies; surgical strategies; vacuum erection device.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding this article.
Figures


References
-
- Lewis R.W., Fugl-Meyer K.S., Bosch R., Fugl-Meyer A.R., Laumann E.O., Lizza E., Martin-Morales A. Definitions, classification, and epidemiology of sexual dysfunction. In: Lue T.F., Basson R., Rosen R., Giuliano F., Khoury S., Montorsi F., editors. Sexual Medicine: Sexual Dysfunction in Men and Women. Health Publications Ltd.; Paris, France: 2004. pp. 37–72.
-
- Meisel R.L., Sachs B.D. The physiology of male sexual behavior. In: Knobil E., Neil J., editors. The Physiology of Reproduction. Raven Press; New York, NY, USA: 1994. pp. 3–96.
-
- Saenz de Tejada I., Angulo J., Cellek S., Gonzalez-Cadavid N.F., Heaton J., Pickard R., Simonsen U. Physiology of erectile function and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. In: Lue T.F., Basson R., Rosen R., Giuliano F., Khoury S., Montorsi F., editors. Sexual Medicine: Sexual Dysfunction in Men and Women. Health Publications Ltd.; Paris, France: 2004. pp. 277–343.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

