Glial Glutamate Transporter Modulation Prevents Development of Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Hyperalgesia and Allodynia in Mice
- PMID: 37239279
- PMCID: PMC10216248
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13050807
Glial Glutamate Transporter Modulation Prevents Development of Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Hyperalgesia and Allodynia in Mice
Abstract
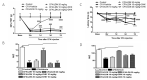
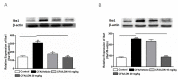
Glial glutamate transporter (GLT-1) modulation in the hippocampus and anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is critically involved in nociceptive pain. The objective of the study was to investigate the effects of 3-[[(2-methylphenyl) methyl] thio]-6-(2-pyridinyl)-pyridazine (LDN-212320), a GLT-1 activator, against microglial activation induced by complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) in a mouse model of inflammatory pain. Furthermore, the effects of LDN-212320 on the protein expression of glial markers, such as ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba1), cluster of differentiation molecule 11b (CD11b), mitogen-activated protein kinases (p38), astroglial GLT-1, and connexin 43 (CX43), were measured in the hippocampus and ACC following CFA injection using the Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence assay. The effects of LDN-212320 on the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in the hippocampus and ACC were also assessed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Pretreatment with LDN-212320 (20 mg/kg) significantly reduced the CFA-induced tactile allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. The anti-hyperalgesic and anti-allodynic effects of LDN-212320 were reversed by the GLT-1 antagonist DHK (10 mg/kg). Pretreatment with LDN-212320 significantly reduced CFA-induced microglial Iba1, CD11b, and p38 expression in the hippocampus and ACC. LDN-212320 markedly modulated astroglial GLT-1, CX43, and, IL-1β expression in the hippocampus and ACC. Overall, these results suggest that LDN-212320 prevents CFA-induced allodynia and hyperalgesia by upregulating astroglial GLT-1 and CX43 expression and decreasing microglial activation in the hippocampus and ACC. Therefore, LDN-212320 could be developed as a novel therapeutic drug candidate for chronic inflammatory pain.
Keywords: LDN-212320; astroglia; chronic pain; glutamate transporter; mice; microglia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

