Efficacy of a Short-Term Lifestyle Change Intervention in Healthy Young Men: The FASt Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 37239539
- PMCID: PMC10218706
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20105812
Efficacy of a Short-Term Lifestyle Change Intervention in Healthy Young Men: The FASt Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
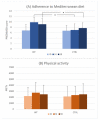
The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of dietary habits and physical activity intervention on lifestyle behavior as a prevention tool supported also by personalized motivational counseling. A two-arm randomized controlled trial was carried out. A sample of 18-22-year-old students was randomly assigned to a four-month intervention based on the Mediterranean diet and moderate physical activity program (N = 66) or to a control group (N = 63). The outcomes were adherence to the Mediterranean diet, physical activity level, and nutrients intake, assessed at enrollment (t0), end of intervention (t4, 4 months after the start), and end of follow-up (t8, 8 months after the start). Adherence to the Mediterranean diet increased from t0 to t4 and t8, more in the intervention (6.83, 9.85, and 9.12, respectively) than in the control group (6.73, 7.00, 7.69, respectively) (p < 0.001). Physical activity showed a moderate increase from t0 to t4 and t8 in both groups, without significant differences between them. Significant differences were seen between the two groups in food intake changes, from t0 to t4 and t8. This randomized controlled trial showed that a moderate short-term intervention based on the Mediterranean diet and regular physical activity determined a positive change in the lifestyle of healthy, normal-weight, young men.
Keywords: Mediterranean diet; adolescence; dietary habits; lifestyle intervention; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Preventing Chronic Diseases: A Vital Investment. WHO Global Report. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2005. [(accessed on 23 March 2023)]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43314.
-
- Willett W., Rockström J., Loken B., Springmann M., Lang T., Vermeulen S., Garnett T., Tilman D., DeClerck F., Wood A., et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT-Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet. 2019;393:447–492. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31788-4. Erratum in Lancet 2019, 393, 530; Erratum in Lancet 2019, 393, 2590; Erratum in Lancet 2020, 395, 338; Erratum in Lancet 2020, 396, e56. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

