Meta-Inflammation and New Anti-Diabetic Drugs: A New Chance to Knock Down Residual Cardiovascular Risk
- PMID: 37239990
- PMCID: PMC10217924
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24108643
Meta-Inflammation and New Anti-Diabetic Drugs: A New Chance to Knock Down Residual Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract
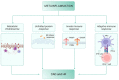
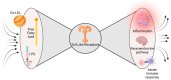
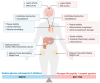
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) represents, with its macro and microvascular complications, one of the most critical healthcare issues for the next decades. Remarkably, in the context of regulatory approval trials, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) proved a reduced incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), i.e., cardiovascular death and heart failure (HF) hospitalizations. The cardioprotective abilities of these new anti-diabetic drugs seem to run beyond mere glycemic control, and a growing body of evidence disclosed a wide range of pleiotropic effects. The connection between diabetes and meta-inflammation seems to be the key to understanding how to knock down residual cardiovascular risk, especially in this high-risk population. The aim of this review is to explore the link between meta-inflammation and diabetes, the role of newer glucose-lowering medications in this field, and the possible connection with their unexpected cardiovascular benefits.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists; meta-inflammation; sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C., Mbanya J.C., et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zelniker T.A., Wiviott S.D., Raz I., Im K., Goodrich E., Bonaca M.P., Mosenzon O., Kato E., Cahn A., Furtado R.H.M., et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet. 2019;393:31–39. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32590-X. Erratum in: Lancet 2019, 393, 30. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kristensen S.L., Rørth R., Jhund P.S., Docherty K.F., Sattar N., Preiss D., Køber L., Petrie M.C., McMurray J.J.V. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7:776–785. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30249-9. Erratum in: Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, e2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilcox T., De Block C., Schwartzbard A.Z., Newman J.D. Diabetic Agents, From Metformin to SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP1 Receptor Agonists: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;75:1956–1974. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.02.056. Erratum in: J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1719–1722. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

