Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Serum Lipid Level Association: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analytic Study
- PMID: 37240018
- PMCID: PMC10218314
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24108675
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Serum Lipid Level Association: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analytic Study
Abstract
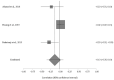
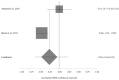
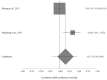
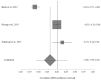
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease with unknown etiology. Many metabolic alterations occur during ALS progress and can be used as a method of pre-diagnostic and early diagnosis. Dyslipidemia is one of the physiological changes observed in numerous ALS patients. The aim of this study is to analyze the possible relationship between the rate of disease progression (functional rating scale (ALS-FRS)) and the plasma lipid levels at the early stage of ALS. A systematic review was carried out in July 2022. The search equation was "Triglycerides AND amyotrophic lateral sclerosis" and its variants. Four meta-analyses were performed. Four studies were included in the meta-analysis. No significant differences were observed between the lipid levels (total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol) and the ALS-FRS score at the onset of the disease. Although the number of studies included in this research was low, the results of this meta-analytic study suggest that there is no clear relationship between the symptoms observed in ALS patients and the plasma lipid levels. An increase in research, as well as an expansion of the geographical area, would be of interest.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; cholesterol; lipids; meta-analysis; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanical ventilation for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 6;10(10):CD004427. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004427.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28982219 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment for sialorrhea (excessive saliva) in people with motor neuron disease/amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD006981. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006981.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593746 Free PMC article.
-
Perampanel for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurol Sci. 2022 Feb;43(2):889-897. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-05867-6. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34994876
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Aminopeptidases as Prognostic Biomarkers in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 12;24(8):7169. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087169. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108335 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for fatigue and weight loss in adults with advanced progressive illness.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD008427. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008427.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 07;4:CD008427. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008427.pub3. PMID: 22258985 Updated.
Cited by
-
Advancements in Pharmacological Interventions and Novel Therapeutic Approaches for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 27;12(10):2200. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102200. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic evidence for the liver-brain axis: lipid metabolism and neurodegenerative disease risk.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Feb 8;24(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02455-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 39923073 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional and Microbiota-Based Approaches in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: From Prevention to Treatment.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 30;17(1):102. doi: 10.3390/nu17010102. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39796536 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marin B., Logroscino G., Boumédiene F., Labrunie A., Couratier P., Babron M.C., Leutenegger A.L., Preux P.M., Beghi E. Clinical and demographic factors and outcome of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in relation to population ancestral origin. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016;31:229–245. doi: 10.1007/s10654-015-0090-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

