Knockout of sws2a and sws2b in Medaka (Oryzias latipes) Reveals Their Roles in Regulating Vision-Guided Behavior and Eye Development
- PMID: 37240129
- PMCID: PMC10218681
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24108786
Knockout of sws2a and sws2b in Medaka (Oryzias latipes) Reveals Their Roles in Regulating Vision-Guided Behavior and Eye Development
Abstract
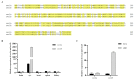
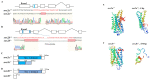
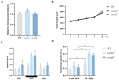
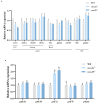
The medaka (Oryzias latipes) is an excellent vertebrate model for studying the development of the retina. Its genome database is complete, and the number of opsin genes is relatively small compared to zebrafish. Short wavelength sensitive 2 (sws2), a G-protein-coupled receptor expressed in the retina, has been lost in mammals, but its role in eye development in fish is still poorly understood. In this study, we established a sws2a and sws2b knockout medaka model by CRISPR/Cas9 technology. We discovered that medaka sws2a and sws2b are mainly expressed in the eyes and may be regulated by growth differentiation factor 6a (gdf6a). Compared with the WT, sws2a-/- and sws2b-/- mutant larvae displayed an increase in swimming speed during the changes from light to dark. We also observed that sws2a-/- and sws2b-/- larvae both swam faster than WT in the first 10 s of the 2 min light period. The enhanced vision-guided behavior in sws2a-/- and sws2b-/- medaka larvae may be related to the upregulation of phototransduction-related genes. Additionally, we also found that sws2b affects the expression of eye development genes, while sws2a is unaffected. Together, these findings indicate that sws2a and sws2b knockouts increase vision-guided behavior and phototransduction, but on the other hand, sws2b plays an important role in regulating eye development genes. This study provides data for further understanding of the role of sws2a and sws2b in medaka retina development.
Keywords: behavior; eye development; medaka; sws2a; sws2b.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of visual opsin repertoire in Medaka (Oryzias latipes).Gene. 2006 Apr 26;371(2):268-78. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.12.005. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16460888
-
Changes in a Cone Opsin Repertoire Affect Color-Dependent Social Behavior in Medaka but Not Behavioral Photosensitivity.Front Genet. 2020 Aug 12;11:801. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00801. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32903371 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Visual Function in Short-Wave-Sensitive 1 (sws1) Gene Knockout Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes) Larvae.Cells. 2023 Aug 28;12(17):2157. doi: 10.3390/cells12172157. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37681889 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and functional characterization of opsins in barfin flounder (Verasper moseri).Gene. 2015 Feb 10;556(2):182-91. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.11.054. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25433330
-
Six6 and Six7 coordinately regulate expression of middle-wavelength opsins in zebrafish.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 5;116(10):4651-4660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1812884116. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30765521 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sws2 Gene Positively Regulates Melanin Production in Plectropomus leopardus Skin via Direct Regulation of the Synthesis of Retinoic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7513. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147513. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archer S. Adaptive Mechanisms in the Ecology of Vision. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 1999. Light and photoreception: Visual pigments and photoreception; pp. 25–42.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

