Calcium Homeostasis, Transporters, and Blockers in Health and Diseases of the Cardiovascular System
- PMID: 37240147
- PMCID: PMC10218565
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24108803
Calcium Homeostasis, Transporters, and Blockers in Health and Diseases of the Cardiovascular System
Abstract
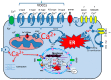
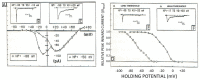
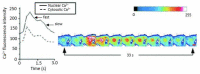
Calcium is a highly positively charged ionic species. It regulates all cell types' functions and is an important second messenger that controls and triggers several mechanisms, including membrane stabilization, permeability, contraction, secretion, mitosis, intercellular communications, and in the activation of kinases and gene expression. Therefore, controlling calcium transport and its intracellular homeostasis in physiology leads to the healthy functioning of the biological system. However, abnormal extracellular and intracellular calcium homeostasis leads to cardiovascular, skeletal, immune, secretory diseases, and cancer. Therefore, the pharmacological control of calcium influx directly via calcium channels and exchangers and its outflow via calcium pumps and uptake by the ER/SR are crucial in treating calcium transport remodeling in pathology. Here, we mainly focused on selective calcium transporters and blockers in the cardiovascular system.
Keywords: Cav1; Cav2; Cav3; G protein; GPCR; L-type calcium channel; N-type calcium channel; P/Q-type calcium channel; R-type calcium channel; T-type calcium channel; calcium; calcium channel blockers; calcium homeostasis; calcium overload; calcium pumps; endoplasmic reticulum; hypercalcemia; mitochondria; nucleus; sodium/calcium exchanger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional importance of T-type voltage-gated calcium channels in the cardiovascular and renal system: news from the world of knockout mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Feb 15;308(4):R227-37. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00276.2014. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25519728 Review.
-
[Pleiotropic effects of new generation calcium channel blockers on cardiovascular protections].Clin Calcium. 2013 Apr;23(4):569-74. Clin Calcium. 2013. PMID: 23545747 Review. Japanese.
-
Molecular biology of calcium channels in the cardiovascular system.Am J Cardiol. 1997 Nov 6;80(9A):17I-22I. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00792-3. Am J Cardiol. 1997. PMID: 9375938 Review.
-
Calcium homeostasis in smooth muscle cells.New Horiz. 1996 Feb;4(1):2-18. New Horiz. 1996. PMID: 8689272 Review.
-
Expression of calcium channel transcripts in the zebrafish heart: dominance of T-type channels.J Exp Biol. 2018 May 20;221(Pt 10):jeb179226. doi: 10.1242/jeb.179226. J Exp Biol. 2018. PMID: 29739832
Cited by
-
Roles of calcium in ameloblasts during tooth development: A scoping review.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2024 Dec 30;20(1):25-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2024.12.010. eCollection 2025 Feb. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39839572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notoginsenoside R1 Attenuates H/R Injury in H9c2 Cells by Maintaining Mitochondrial Homeostasis.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 10;47(1):44. doi: 10.3390/cimb47010044. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39852159 Free PMC article.
-
The Dysfunction of Ca2+ Channels in Hereditary and Chronic Human Heart Diseases and Experimental Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 27;24(21):15682. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115682. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic insights into the effect of trace elements on cardiovascular diseases: multi-omics Mendelian randomization combined with linkage disequilibrium score regression analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 3;15:1459465. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1459465. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39691718 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Impact of the Use of Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 20;13(8):2404. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082404. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38673676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bkaily G., Al-Khoury J., Simon Y., Jacques D. Intracellular Free Calcium Measurement Using Confocal Imaging. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017;1527:177–187. - PubMed
-
- Bkaily G., Avedanian L., Al-Khoury J., Chamoun M., Semaan R., Jubinville-Leblanc C., D’Orléans-Juste P., Jacques D. Nuclear membrane R-type calcium channels mediate cytosolic ET-1-induced increase of nuclear calcium in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015;93:291–297. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0519. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jacques D.B. Cardiovascular physiopathology of angiotensin II and its plasma and nuclear envelop membrane’s receptors. In: Dhalla N.S., Bhullar S.K., Shah A.K., editors. The Renin Angiotensin System in Cardiovascular Disease. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2023. pp. 63–80. Advances in Biochemistry in Health and Disease.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

