Asymmetric Dimethylation of Ribosomal S6 Kinase 2 Regulates Its Cellular Localisation and Pro-Survival Function
- PMID: 37240151
- PMCID: PMC10218830
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24108806
Asymmetric Dimethylation of Ribosomal S6 Kinase 2 Regulates Its Cellular Localisation and Pro-Survival Function
Abstract
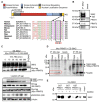
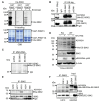
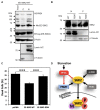
Ribosomal S6 kinases (S6Ks) are critical regulators of cell growth, homeostasis, and survival, with dysregulation of these kinases found to be associated with various malignancies. While S6K1 has been extensively studied, S6K2 has been neglected despite its clear involvement in cancer progression. Protein arginine methylation is a widespread post-translational modification regulating many biological processes in mammalian cells. Here, we report that p54-S6K2 is asymmetrically dimethylated at Arg-475 and Arg-477, two residues conserved amongst mammalian S6K2s and several AT-hook-containing proteins. We demonstrate that this methylation event results from the association of S6K2 with the methyltransferases PRMT1, PRMT3, and PRMT6 in vitro and in vivo and leads to nuclear the localisation of S6K2 that is essential to the pro-survival effects of this kinase to starvation-induced cell death. Taken together, our findings highlight a novel post-translational modification regulating the function of p54-S6K2 that may be particularly relevant to cancer progression where general Arg-methylation is often elevated.
Keywords: AT-hook; SCLC; arginine methylation; methyltransferases; serine/threonine kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
S6 kinase 2 is bound to chromatin-nuclear matrix cellular fractions and is able to phosphorylate histone H3 at threonine 45 in vitro and in vivo.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Jun;115(6):1048-62. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24566. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 23564320
-
S6K1(-/-)/S6K2(-/-) mice exhibit perinatal lethality and rapamycin-sensitive 5'-terminal oligopyrimidine mRNA translation and reveal a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent S6 kinase pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Apr;24(8):3112-24. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.8.3112-3124.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15060135 Free PMC article.
-
The polyproline-motif of S6K2: eIF5A translational dependence and importance for protein-protein interactions.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):6015-6025. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27888. Epub 2018 Oct 15. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30320934
-
Functions and regulation of the 70kDa ribosomal S6 kinases.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Jan;43(1):47-59. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.09.018. Epub 2010 Oct 12. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 20932932 Review.
-
S6K2 promises an important therapeutic potential for cancer.Future Oncol. 2019 Jan;15(1):95-102. doi: 10.2217/fon-2018-0332. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Future Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30730779 Review.
Cited by
-
S6K2 in Focus: Signaling Pathways, Post-Translational Modifications, and Computational Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 28;26(1):176. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010176. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pardo O.E., Wellbrock C., Khanzada U.K., Aubert M., Arozarena I., Davidson S., Bowen F., Parker P.J., Filonenko V.V., Gout I.T., et al. FGF-2 protects small cell lung cancer cells from apoptosis through a complex involving PKCepsilon, B-Raf and S6K2. EMBO J. 2006;25:3078–3088. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601198. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Valovka T., Verdier F., Cramer R., Zhyvoloup A., Fenton T., Rebholz H., Wang M.-L., Gzhegotsky M., Lutsyk A., Matsuka G., et al. Protein kinase C phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6 kinase betaII and regulates its subcellular localization. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;23:852–863. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.3.852-863.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

