Pro-Osteogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Synergistic Effect of Orthosilicic Acid, Vitamin K2, Curcumin, Polydatin and Quercetin Combination in Young and Senescent Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
- PMID: 37240169
- PMCID: PMC10218531
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24108820
Pro-Osteogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Synergistic Effect of Orthosilicic Acid, Vitamin K2, Curcumin, Polydatin and Quercetin Combination in Young and Senescent Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Abstract
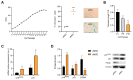
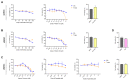
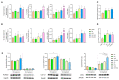
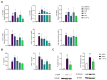
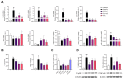
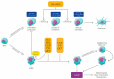
During aging, bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs)-the precursors of osteoblasts-undergo cellular senescence, losing their osteogenic potential and acquiring a pro-inflammatory secretory phenotype. These dysfunctions cause bone loss and lead to osteoporosis. Prevention and intervention at an early stage of bone loss are important, and naturally active compounds could represent a valid help in addition to diet. Here, we tested the hypothesis that the combination of two pro-osteogenic factors, namely orthosilicic acid (OA) and vitamin K2 (VK2), and three other anti-inflammatory compounds, namely curcumin (CUR), polydatin (PD) and quercetin (QCT)-that mirror the nutraceutical BlastiMin Complex® (Mivell, Italy)-would be effective in promoting MSC osteogenesis, even of replicative senescent cells (sMSCs), and inhibiting their pro-inflammatory phenotype in vitro. Results showed that when used at non-cytotoxic doses, (i) the association of OA and VK2 promoted MSC differentiation into osteoblasts, even when cultured without other pro-differentiating factors; and (ii) CUR, PD and QCT exerted an anti-inflammatory effect on sMSCs, and also synergized with OA and VK2 in promoting the expression of the pivotal osteogenic marker ALP in these cells. Overall, these data suggest a potential role of using a combination of all of these natural compounds as a supplement to prevent or control the progression of age-related osteoporosis.
Keywords: inflammaging; mesenchymal stromal cells; natural compounds; osteogenesis; osteoporosis; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manu- script; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

