RNA-Seq Analysis Reveals an Essential Role of the cGMP-PKG-MAPK Pathways in Retinal Degeneration Caused by Cep250 Deficiency
- PMID: 37240188
- PMCID: PMC10218315
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24108843
RNA-Seq Analysis Reveals an Essential Role of the cGMP-PKG-MAPK Pathways in Retinal Degeneration Caused by Cep250 Deficiency
Abstract
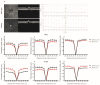
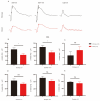
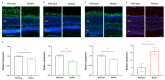
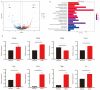
Usher syndrome (USH) is characterised by degenerative vision loss known as retinitis pigmentosa (RP), sensorineural hearing loss, and vestibular dysfunction. RP can cause degeneration and the loss of rod and cone photoreceptors, leading to structural and functional changes in the retina. Cep250 is a candidate gene for atypical Usher syndrome, and this study describes the development of a Cep250 KO mouse model to investigate its pathogenesis. OCT and ERG were applied in Cep250 and WT mice at P90 and P180 to access the general structure and function of the retina. After recording the ERG responses and OCT images at P90 and P180, the cone and rod photoreceptors were visualised using an immunofluorescent stain. TUNEL assays were applied to observe the apoptosis in Cep250 and WT mice retinas. The total RNA was extracted from the retinas and executed for RNA sequencing at P90. Compared with WT mice, the thickness of the ONL, IS/OS, and whole retina of Cep250 mice was significantly reduced. The a-wave and b-wave amplitude of Cep250 mice in scotopic and photopic ERG were lower, especially the a-wave. According to the immunostaining and TUNEL stain results, the photoreceptors in the Cep250 retinas were also reduced. An RNA-seq analysis showed that 149 genes were upregulated and another 149 genes were downregulated in Cep250 KO retinas compared with WT mice retinas. A KEGG enrichment analysis indicated that cGMP-PKG signalling pathways, MAPK signalling pathways, edn2-fgf2 axis pathways, and thyroid hormone synthesis were upregulated, whereas protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum was downregulated in Cep250 KO eyes. Cep250 KO mice experience a late-stage retinal degeneration that manifests as the atypical USH phenotype. The dysregulation of the cGMP-PKG-MAPK pathways may contribute to the pathogenesis of cilia-related retinal degeneration.
Keywords: Cep250-KO mice; RNA sequencing; Usher syndrome; cGMP-PKG-MAPK signalling pathways; retinal degeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Homozygous Knockout of Cep250 Leads to a Relatively Late-Onset Retinal Degeneration and Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Mice.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 Mar 1;12(3):3. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.3.3. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 36857066 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated Arginine Metabolism Is Linked to Retinal Degeneration in Cep250 Knockout Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Sep 1;64(12):2. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.12.2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37656476 Free PMC article.
-
cGMP-PKG dependent transcriptome in normal and degenerating retinas: Novel insights into the retinitis pigmentosa pathology.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Nov;212:108752. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108752. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 34478738
-
Molecular basis of human Usher syndrome: deciphering the meshes of the Usher protein network provides insights into the pathomechanisms of the Usher disease.Exp Eye Res. 2006 Jul;83(1):97-119. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.11.010. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Exp Eye Res. 2006. PMID: 16545802 Review.
-
Usher syndrome: Hearing loss, retinal degeneration and associated abnormalities.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Mar;1852(3):406-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.11.020. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25481835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schneider N., Sundaresan Y., Gopalakrishnan P., Beryozkin A., Hanany M., Levanon E.Y., Banin E., Ben-Aroya S., Sharon D. Inherited retinal diseases: Linking genes, disease-causing variants, and relevant therapeutic modalities. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2022;89:101029. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101029. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82101176/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- LTGD23H120002/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province
- 2021C03102/Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province
- 2023KY151/Health Technology Plan Project in Zhejiang Province
- 2021KY808/Health Technology Plan Project in Zhejiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

