Thromboembolic Complications in Adult Patients Following Fontan Procedure-A Multicenter Study
- PMID: 37240571
- PMCID: PMC10219158
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12103465
Thromboembolic Complications in Adult Patients Following Fontan Procedure-A Multicenter Study
Abstract
Background: Morbidity and mortality following Fontan (FO) surgery are primarily thromboembolic in nature. However, follow-up data regarding thromboembolic complications (TECs) in adult patients after FO procedure are inconsistent. In this multicenter study, we investigated the incidence of TECs in FO patients.
Methods: We studied 91 patients who underwent FO procedure. Clinical data, laboratory, and imaging investigations were collected prospectively during the scheduled medical appointments in 3 Adult Congenital Heart Disease Departments in Poland. TECs were recorded during a median follow-up of 31 months.
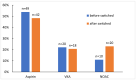
Results: Four patients (4.4%) were lost to follow-up. The mean age of patients was 25.3 (±6.0) years at enrollment, and the mean time between FO operation and investigation was 22.1 (±5.1) years. A total of 21 out of 91 patients (23.1%) had a history of 24 TECs since an FO procedure, mainly pulmonary embolism (PE; n = 12, 13.2%), including 4 (33.3%) silent PE. The mean time since FO operation to the first TEC was 17.8 (±5.1) years. During follow-up, we documented 9 TECs in 7 (8.0%) patients, mainly PE (n = 5, 5.5%). Most patients with TEC had a left type of systemic ventricle (57.1%). Three patients (42.9%) were treated with aspirin, 3 (3.4%) with Vitamin K antagonists or novel oral anticoagulants, and 1 patient had no antithrombotic treatment at the time of TEC occurrence. Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias were present in 3 patients (42.9%).
Conclusions: This prospective study shows that TECs are common in FO patients, and a significant number of these events occur during adolescence and young adulthood. We also indicated how much TECs are underestimated in the growing adult FO population. The complexity of the problem requires more studies, especially to standardize the prevention of TECs in the whole FO population.
Keywords: Fontan procedure; follow-up; thromboembolic complications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Monagle P., Cochrane A., Roberts R., Manlhiot C., Weintraub R., Szechtman B., Hughes M., Andrew M., McCrindle B.W., Fontan Anticoagulation Study Group Multicenter, randomized trial comparing heparin/warfarin and acetylsalicylic acid as primary thromboprophylaxis for 2 years after the Fontan procedure in children. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011;58:645–651. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.01.061. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gissel M., Tomkiewicz-Pajak L., Podolec P., Hoffman P., Trojnarska O., Lipczyńska M., Undas A., Brummel-Ziedins K.E. In silico thrombin and factor Xa generation profiles in adult patients after Fontan operation. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis. 2018;29:236–240. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000694. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources