Fabricated High-Strength, Low-Elastic Modulus Biomedical Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn Alloy via Powder Metallurgy
- PMID: 37241471
- PMCID: PMC10222908
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16103845
Fabricated High-Strength, Low-Elastic Modulus Biomedical Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn Alloy via Powder Metallurgy
Abstract
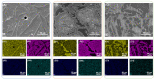
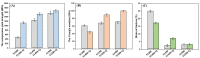
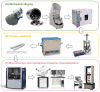
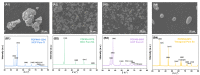
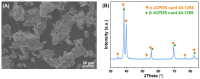
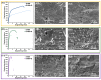
With the huge demands of an aging society, it is urgent to develop a new generation of non-toxic titanium alloy to match the modulus of human bone. Here, we prepared bulk Ti2448 alloys by powder metallurgy technology, and focused on the influence of the sintering process on the porosity, phase composition, and mechanical properties of the initial sintered samples. Furthermore, we performed solution treatment on the samples under different sintering parameters to further adjust the microstructure and phase composition, so as to achieve strength enhancement and reduction of Young's modulus. Solution treatment can effectively inhibit the continuous α phase precipitated along the grain boundaries of the β matrix, which is beneficial to the fracture resistance. Therefore, the water-quenched sample exhibits good mechanical properties due to the absence of acicular α-phase. Samples sintered at 1400 °C and subsequently water quenched have excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, which benefit from high porosity and the smaller feature size of microstructure. To be specific, the compressive yield stress is 1100 MPa, the strain at fracture is 17.5%, and the Young's modulus is 44 GPa, which are more applicable to orthopedic implants. Finally, the relatively mature sintering and solution treatment process parameters were screened out for reference in actual production.
Keywords: Ti2448 alloy; mechanical properties; microstructure analysis; porosity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Heat Treatments of Metastable β Titanium Alloy Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn Processed by Laser Powder Bed Fusion.Materials (Basel). 2022 May 25;15(11):3774. doi: 10.3390/ma15113774. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35683075 Free PMC article.
-
Alloy Design and Fabrication of Duplex Titanium-Based Alloys by Spark Plasma Sintering for Biomedical Implant Applications.Materials (Basel). 2022 Dec 1;15(23):8562. doi: 10.3390/ma15238562. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36500058 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoblast cellular activity on low elastic modulus Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn alloy.Dent Mater. 2017 Feb;33(2):152-165. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Dent Mater. 2017. PMID: 27889088
-
Impact of scandium on mechanical properties, corrosion behavior, friction and wear performance, and cytotoxicity of a β-type Ti-24Nb-38Zr-2Mo alloy for orthopedic applications.Acta Biomater. 2021 Oct 15;134:791-803. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.07.061. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34332105
-
Research Progress on Cu-15Ni-8Sn Alloys: The Effect of Microalloying and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties.Materials (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;16(17):5913. doi: 10.3390/ma16175913. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dai N., Zhang L.-C., Zhang J., Chen Q., Wu M. Corrosion behavior of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4 V alloy in NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2016;102:484–489. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.10.041. - DOI
-
- Liu Y., Wang H., Li S., Wang S., Wang W., Hou W., Hao Y., Yang R., Zhang L. Compressive and fatigue behavior of beta-type titanium porous structures fabricated by electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 2017;126:58–66. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.12.052. - DOI
-
- Li J., Bai Y., Fan Z., Li S., Hao Y., Yang R., Gao Y. Effect of fluoride on the corrosion behavior of nanostructured Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn alloy in acidulated artificial saliva. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018;34:1660–1670. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2018.01.008. - DOI
-
- Abd-elrhman Y., Gepreel M.A.H., Abdel-Moniem A., Kobayashi S. Compatibility assessment of new V-free low-cost Ti–4.7Mo–4.5Fe alloy for some biomedical applications. Mater. Des. 2016;97:445–453. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.02.110. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

