Construction of Bio-TiO2/Algae Complex and Synergetic Mechanism of the Acceleration of Phenol Biodegradation
- PMID: 37241509
- PMCID: PMC10221352
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16103882
Construction of Bio-TiO2/Algae Complex and Synergetic Mechanism of the Acceleration of Phenol Biodegradation
Abstract
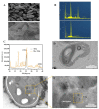
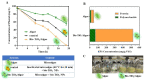
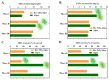
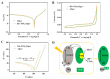
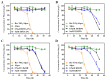
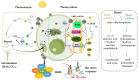
Microalgae have been widely employed in water pollution treatment since they are eco-friendly and economical. However, the relatively slow treatment rate and low toxic tolerance have seriously limited their utilization in numerous conditions. In light of the problems above, a novel biosynthetic titanium dioxide (bio-TiO2 NPs)-microalgae synergetic system (Bio-TiO2/Algae complex) has been established and adopted for phenol degradation in the study. The great biocompatibility of bio-TiO2 NPs ensured the collaboration with microalgae, improving the phenol degradation rate by 2.27 times compared to that with single microalgae. Remarkably, this system increased the toxicity tolerance of microalgae, represented as promoted extracellular polymeric substances EPS secretion (5.79 times than single algae), and significantly reduced the levels of malondialdehyde and superoxide dismutase. The boosted phenol biodegradation with Bio-TiO2/Algae complex may be attributed to the synergetic interaction of bio-TiO2 NPs and microalgae, which led to the decreased bandgap, suppressed recombination rate, and accelerated electron transfer (showed as low electron transfer resistance, larger capacitance, and higher exchange current density), resulting in increased light energy utilization rate and photocatalytic rate. The results of the work provide a new understanding of the low-carbon treatment of toxic organic wastewater and lay a foundation for further remediation application.
Keywords: TiO2; biodegradation; biosynthesis; microalgae; photocatalysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Visible-light-driven synergistic photocatalysis-microbial metabolism by Chlorella ellipsoidea@TiO2-Ag-AgCl nano-biohybrid: Enhanced o-cresol biodegradation and mechanistic insights.J Hazard Mater. 2025 May 31;495:138771. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.138771. Online ahead of print. J Hazard Mater. 2025. PMID: 40483951
-
TiO2 nanoparticles in seawater: Aggregation and interactions with the green alga Dunaliella tertiolecta.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Feb;148:184-193. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.10.024. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 29055202
-
Toxicity of TiO2, in nanoparticle or bulk form to freshwater and marine microalgae under visible light and UV-A radiation.Environ Pollut. 2017 Aug;227:39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.053. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Environ Pollut. 2017. PMID: 28454020
-
Potential Application of Algae in Biodegradation of Phenol: A Review and Bibliometric Study.Plants (Basel). 2021 Dec 6;10(12):2677. doi: 10.3390/plants10122677. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34961148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technical insights into the production of green fuel from CO2 sequestered algal biomass: A conceptual review on green energy.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Feb 10;755(Pt 2):142636. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142636. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33065504 Review.
Cited by
-
Visible Light Enhancement of Biocarbon Quantum-Dot-Decorated TiO2 for Naphthalene Removal.Molecules. 2024 Jun 6;29(11):2708. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112708. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893581 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the potential of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: an insight into green synthesis, optimizations, characterizations, and multifunctional applications.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Dec 23;23(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02609-5. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39710687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Said K.A.M., Ismail A.F., Karim Z.A., Abdullah M.S., Hafeez A. A review of technologies for the phenolic compounds recovery and phenol removal from wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021;151:257–289. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.05.015. - DOI
-
- Villegas L.G.C., Mashhadi N., Chen M., Mukherjee D., Taylor K.E., Biswas N. A Short Review of Techniques for Phenol Removal from Wastewater. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016;2:157–167. doi: 10.1007/s40726-016-0035-3. - DOI
-
- Mohammadi S., Kargari A., Sanaeepur H., Abbassian K., Najafi A., Mofarrah E. Phenol removal from industrial wastewaters: A short review. Desalination Water Treat. 2014;53:2215–2234. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2014.883327. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

