Determination of Phosphodiesterase Type-5 Inhibitors (PDE-5) in Dietary Supplements
- PMID: 37241857
- PMCID: PMC10221795
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28104116
Determination of Phosphodiesterase Type-5 Inhibitors (PDE-5) in Dietary Supplements
Abstract
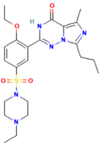
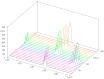
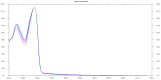
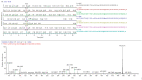
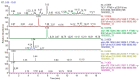
This study proposed a high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) screening method to detect phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors as possible adulterant agents in various dietary supplements. Chromatographic analysis was performed on silica gel 60F254 plates using a mixture of ethyl acetate:toluene:methanol:ammonia in a volume ratio of 50:30:20:0.5 as a mobile phase. The system provided compact spots and symmetrical peaks of sildenafil and tadalafil with retardation factor values of 0.55 and 0.90, respectively. The analysis of products purchased from the internet or specialized stores demonstrated the presence of sildenafil, tadalafil, or both compounds in 73.3% of products, highlighting inadequacies and inconsistencies in the labeling, as all dietary supplements were declared to be natural. The results were confirmed using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a positive electrospray ionization high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS-MS) method. Furthermore, in some samples, vardenafil and various analogs of PDE-5 inhibitors were detected using a non-target HRMS-MS approach. The results of the quantitative analysis revealed similar findings between the two methods, with adulterant quantities found to be similar to or higher than those in approved medicinal products. This study demonstrated that the HPTLC method is a suitable and economical method for screening PDE-5 inhibitors as adulterants in dietary supplements intended for sexual activity enhancement.
Keywords: HPTLC; UHPLC-HRMS-MS; adulterants; dietary supplements; sildenafil; tadalafil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Fode M., Wiborg M.H., Fojecki G., Joensen U.N., Jensen C.F.S. Organic erectile dysfunction. Ugeskr. Laeger. 2020;182:V09190546. - PubMed
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 135398744, Sildenafil. [(accessed on 17 February 2023)]; Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Sildenafil.
-
- Žuntar I., Krivohlavek A., Kosić-Vukšić J., Granato D., Kovačević D.B., Putnik P. Pharmacological and toxicological health risk of food (herbal) supplements adulterated with erectile dysfunction medications. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018;24:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2018.10.012. - DOI
-
- Sifuma S.W.A., Mwangi J.W., Mutai P.C., Ongarora D.B., Njuguna N.M. Evaluation of adulteration of herbal medicine used for treatment of erectile dysfunction in Nairobi County, Kenya. IJPSR. 2022;13:2095–2100.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

