In Silico Drug Design of Anti-Breast Cancer Agents
- PMID: 37241915
- PMCID: PMC10223712
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28104175
In Silico Drug Design of Anti-Breast Cancer Agents
Abstract
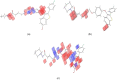
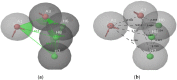
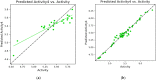
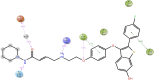
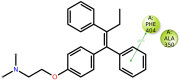
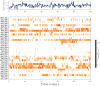
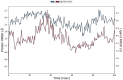
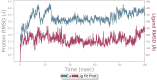
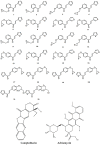
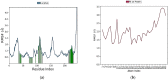
Cancer is a condition marked by abnormal cell proliferation that has the potential to invade or indicate other health issues. Human beings are affected by more than 100 different types of cancer. Some cancer promotes rapid cell proliferation, whereas others cause cells to divide and develop more slowly. Some cancers, such as leukemia, produce visible tumors, while others, such as breast cancer, do not. In this work, in silico investigations were carried out to investigate the binding mechanisms of four major analogs, which are marine sesquiterpene, sesquiterpene lactone, heteroaromatic chalcones, and benzothiophene against the target estrogen receptor-α for targeting breast cancer using Schrödinger suite 2021-4. The Glide module handled the molecular docking experiments, the QikProp module handled the ADMET screening, and the Prime MM-GB/SA module determined the binding energy of the ligands. The benzothiophene analog BT_ER_15f (G-score -15.922 Kcal/mol) showed the best binding activity against the target protein estrogen receptor-α when compared with the standard drug tamoxifen which has a docking score of -13.560 Kcal/mol. TRP383 (tryptophan) has the highest interaction time with the ligand, and hence it could act for a long time. Based on in silico investigations, the benzothiophene analog BT_ER_15f significantly binds with the active site of the target protein estrogen receptor-α. Similar to the outcomes of molecular docking, the target and ligand complex interaction motif established a high affinity of lead candidates in a dynamic system. This study shows that estrogen receptor-α targets inhibitors with better potential and low toxicity when compared to the existing market drugs, which can be made from a benzothiophene derivative. It may result in considerable activity and be applied to more research on breast cancer.
Keywords: 3D-QSAR; benzothiophene analog; breast cancer; docking studies; molecular dynamics; pharmacophore modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
In Silico Studies of Phytoconstituents to Identify Potential Inhibitors for ERα Protein of Breast Cancer.Med Chem. 2025;21(2):144-159. doi: 10.2174/0115734064301748240821081206. Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40007185
-
In-silico Design, ADMET Screening, MM-GBSA Binding Free Energy of Some Novel Isoxazole Substituted 9-Anilinoacridines as HER2 Inhibitors Targeting Breast Cancer.Curr Drug Res Rev. 2019;11(2):118-128. doi: 10.2174/2589977511666190912154817. Curr Drug Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 31513003
-
Artonin E and Structural Analogs from Artocarpus Species Abrogates Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer.Molecules. 2016 Jun 29;21(7):839. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070839. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27367662 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting in the estrogen receptor hormonal pathway.Semin Oncol. 2004 Feb;31(1 Suppl 3):28-38. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2004.01.004. Semin Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15052541 Review.
-
Integrating biocomputational techniques for Breast cancer drug discovery via the HER-2, BCRA, VEGF and ER protein targets.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Jan;168:107737. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107737. Epub 2023 Nov 19. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38000249 Review.
Cited by
-
Rationally Designed Novel Antimicrobial Peptides Targeting Chitin Synthase for Combating Soybean Phytophthora Blight.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 20;25(6):3512. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063512. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542484 Free PMC article.
-
Acridine-Based Chalcone 1C and ABC Transporters.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 27;26(9):4138. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094138. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362377 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual screening, in silico pharmacokinetic and toxicity profiling of colchicine-based inhibitors of estrogen receptor of breast cancer.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Jan 25;14:101926. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101926. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39968053 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Studies of Phytoconstituents to Identify Potential Inhibitors for ERα Protein of Breast Cancer.Med Chem. 2025;21(2):144-159. doi: 10.2174/0115734064301748240821081206. Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40007185
References
-
- Feng Y., Spezia M., Huang S., Yuan C., Zeng Z., Zhang L., Ji X., Liu W., Huang B., Luo W., et al. Breast cancer development and progression: Risk factors, cancer stem cells, signaling pathways, genomics, and molecular pathogenesis. Genes Dis. 2018;5:77–106. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2018.05.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bisoyi P. Understanding Cancer. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2022. [(accessed on 13 March 2023)]. Malignant Tumors—As Cancer; pp. 21–36. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780323998833000111.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

