Magnesium Deficiency and Cardiometabolic Disease
- PMID: 37242238
- PMCID: PMC10222666
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15102355
Magnesium Deficiency and Cardiometabolic Disease
Abstract
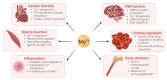
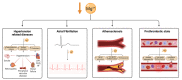
Magnesium (Mg2+) has many physiological functions within the body. These include important roles in maintaining cardiovascular functioning, where it contributes to the regulation of cardiac excitation-contraction coupling, endothelial functioning and haemostasis. The haemostatic roles of Mg2+ impact upon both the protein and cellular arms of coagulation. In this review, we examine how Mg2+ homeostasis is maintained within the body and highlight the various molecular roles attributed to Mg2+ in the cardiovascular system. In addition, we describe how nutritional and/or disease-associated magnesium deficiency, seen in some metabolic conditions, has the potential to influence cardiac and vascular outcomes. Finally, we also examine the potential for magnesium supplements to be employed in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disorders and in the management of cardiometabolic health.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; magnesium; metal ion dyshomeostasis; nutrient deficiency; supplementation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rude R. Magnesium disorders. In: Kokko J., Tannen R., editors. Fluids and Electrolytes. W.B. Saunders Company; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 1996. pp. 421–445.
-
- Rosanoff A., West C., Elin R., Micke O., Baniasadi S., Barbagallo M., Campbell E., Cheng F.C., Costello R.B., Gamboa-Gomez C., et al. Recommendation on an updated standardization of serum magnesium reference ranges. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022;61:3697–3706. doi: 10.1007/s00394-022-02916-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Micke O., Vormann J., Kraus A., Kisters K. Serum magnesium: Time for a standardized and evidence-based reference range. Magnes. Res. 2021;34:84–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

