Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Rosebud Extracts of Newly Crossbred Roses
- PMID: 37242259
- PMCID: PMC10223673
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15102376
Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Rosebud Extracts of Newly Crossbred Roses
Abstract
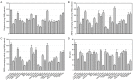
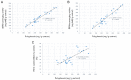
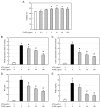
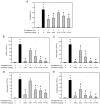
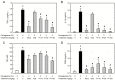
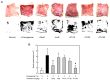
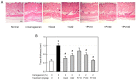
Oxidative stress and inflammation are basic pathogenic factors involved in tissue injury and pain, as well as acute and chronic diseases. Since long-term uses of synthetic steroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause severe adverse effects, novel effective materials with minimal side effects are required. In this study, polyphenol content and antioxidative activity of rosebud extracts from 24 newly crossbred Korean roses were analyzed. Among them, Pretty Velvet rosebud extract (PVRE) was found to contain high polyphenols and to show in vitro antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities. In RAW 264.7 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), PVRE down-regulated mRNA expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and thereby decreased nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production. In a subcutaneous air-pouch inflammation model, treatment with PVRE decreased λ-carrageenan-induced tissue exudation, infiltration of inflammatory cells, and inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β concentrations, as achieved with dexamethasone (a representative steroid). Notably, PVRE also inhibited PGE2, similar to dexamethasone and indomethacin (a representative NSAID). The anti-inflammatory effects of PVRE were confirmed by microscopic findings, attenuating tissue erythema, edema, and inflammatory cell infiltration. These results indicate that PVRE exhibits dual (steroid- and NSAID-like) anti-inflammatory activities by blocking both the iNOS-NO and COX-2-PG pathways, and that PVRE could be a potential candidate as an anti-inflammatory material for diverse tissue injuries.
Keywords: Pretty Velvet; anti-inflammation; antioxidation; nitric oxide; polyphenol; prostaglandin E2; rosebud extract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ethyl acetate fraction from Nymphaea hybrida Peck modulates inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and acute inflammation murine models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113698. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113698. Epub 2020 Dec 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33338590
-
Exploring the anti-inflammatory potential of Colocasia esculenta root extract in in-vitro and in-vivo models of inflammation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;303:116021. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.116021. Epub 2022 Dec 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36516907
-
Anti-inflammatory and antitumoural effects of Uncaria guianensis bark.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):1154-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.055. Epub 2013 Nov 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24212077
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous extract of Centipeda minima.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 May 20;147(2):395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.03.025. Epub 2013 Mar 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23506988
-
Amelioration of TPA-induced skin inflammation by the leaf extract of Vernonia amygdalina involves ERK/STAT3 (Ser727) signaling inhibition.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jul 20;102:154194. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154194. Epub 2022 May 23. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35660348
Cited by
-
In Vitro Inhibitory Mechanism of Polyphenol Extracts from Multi-Frequency Power Ultrasound-Pretreated Rose Flower Against α-Glucosidase.Foods. 2024 Oct 27;13(21):3421. doi: 10.3390/foods13213421. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39517205 Free PMC article.
-
An active ingredient from the combination of Corydalis Rhizoma and Paeoniae Radix Alba relieves chronic compression injury-induced pain in rats by ameliorating AR/Mboat2-mediated ferroptosis in spinal cord neurons.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 25;16:1558916. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1558916. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40201699 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

