Angelica keiskei Impacts the Lifespan and Healthspan of Drosophila melanogaster in a Sex and Strain-Dependent Manner
- PMID: 37242522
- PMCID: PMC10222730
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16050738
Angelica keiskei Impacts the Lifespan and Healthspan of Drosophila melanogaster in a Sex and Strain-Dependent Manner
Abstract
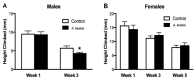
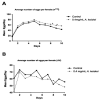
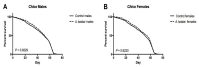
Angelica keiskei is a perennial plant, belonging to the Apiaceae family and originating from Japan. This plant has been reported to act as a diuretic, analeptic, antidiabetic, hypertensive, tumor, galactagogue, and laxative. The mechanism of action of A. keiskei is not known, but previous studies have suggested that it may act as an antioxidant. In this work, we used Drosophila melanogaster to evaluate the impact of A. keiskei on lifespan and healthspan and its potential anti-aging mechanism by conducting multiple assays on three fly strains: w1118, chico, and JIV. We observed that the extract extended lifespan and improved healthspan in a sex- and strain-dependent manner. A. keiskei extended lifespan and improved reproductive fitness in female flies and either had no effect or decreased survival and physical performance in males. The extract protected against the superoxide generator paraquat in both sexes. These sex-specific effects suggest that A. keiskei may act through age-specific pathways such as the insulin and insulin-like growth factor signaling (IIS) pathways. Upon examination, we found that the increased survival of A. keiskei-fed females was dependent on the presence of the insulin receptor substrate chico, supporting the role of IIS in the action of A. keiskei.
Keywords: Angelica keiskei; Apiaceae; Drosophila melanogaster; healthspan; insulin/IGF-1 pathway; lifespan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Amalia R., Aulifa D.L., Zain D.N., Pebiansyah A., Levita J. The Cytotoxicity and Nephroprotective Activity of the Ethanol Extracts of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi Stems and Leaves against the NAPQI-Induced Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK293) Cell Line. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021;2021:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2021/6458265. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

