Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) Related Drugs in Pain Management
- PMID: 37242543
- PMCID: PMC10224460
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16050760
Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) Related Drugs in Pain Management
Abstract
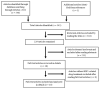
Objective. The aim of this review is to explore the role of IGF-1 and IGF-1R inhibitors in pain-related conditions and assess the effectiveness of IGF-1-related drugs in pain management. Specifically, this paper investigates the potential involvement of IGF-1 in nociception, nerve regeneration, and the development of neuropathic pain. Methods. We conducted a search of the PUBMED/MEDLINE database, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library for all reports published in English on IGF-1 in pain management from origination through November 2022. The resulting 545 articles were screened, and 18 articles were found to be relevant after reading abstracts. After further examination of the full text of these articles, ten were included in the analysis and discussion. The levels of clinical evidence and implications for recommendations of all the included human studies were graded. Results. The search yielded 545 articles, of which 316 articles were deemed irrelevant by reading the titles. There were 18 articles deemed relevant after reading abstracts, of which 8 of the reports were excluded due to lack of IGF-1-related drug treatment after reviewing the full text of the articles. All ten articles were retrieved for analysis and discussion. We found that IGF-1 may have several positive effects on pain management, including promoting the resolution of hyperalgesia, preventing chemotherapy-induced neuropathy, reversing neuronal hyperactivity, and elevating the nociceptive threshold. On the other hand, IGF-1R inhibitors may alleviate pain in mice with injury of the sciatic nerve, bone cancer pain, and endometriosis-induced hyperalgesia. While one study showed marked improvement in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy in humans treated with IGF-1R inhibitor, two other studies did not find any benefits from IGF-1 treatment. Conclusions. This review highlights the potential of IGF-1 and IGF-1R inhibitors in pain management, but further research is needed to fully understand their efficacy and potential side effects.
Keywords: IGF-1; IGF-1R inhibitor; pain management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Leal-Cerro A., Povedano J., Astorga R., Gonzalez M., Silva H., García-Pesquera F., Casanueva F.F., Diéguez C. The growth hormone (GH)-releasing hormone-GH-insulin-like growth factor-1 axis in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999;84:3378–3381. doi: 10.1210/jc.84.9.3378. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous