Canagliflozin Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Autistic-like Features in Valproic-Acid-Induced Autism in Rats: Comparison with Aripiprazole Action
- PMID: 37242552
- PMCID: PMC10224524
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16050769
Canagliflozin Ameliorates Oxidative Stress and Autistic-like Features in Valproic-Acid-Induced Autism in Rats: Comparison with Aripiprazole Action
Abstract
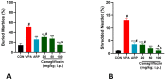
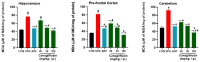
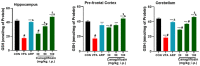
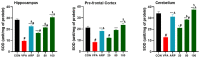
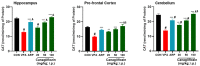
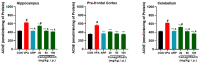
Based on their proven anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, recent studies have examined the therapeutic potential of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Therefore, the aim of this study is to assess the effects of subchronic systemic treatment with intraperitoneal (i.p.) canagliflozin (20, 50, and 100 mg/kg) compared to aripiprazole (ARP) (3 mg/g, i.p.) in a valproic acid (VPA)-induced rat model of autism. The behavioral characteristics of ASD, oxidative stress, and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity in rats with ASD-like behaviors, which were induced by prenatal exposure to VPA, were evaluated. The behavioral assessment methods used for this study were the open field test (OFT), the marble-burying test (MBT), and the nestlet-shredding test (NST) to examine their exploratory, anxiety, and compulsiveness-like actions, while the biochemical assessment used for this study was an ELISA colorimetric assay to measure ASD biomarker activity in the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and cerebellum. Rats that were pretreated with 100 mg/kg of canagliflozin displayed a significantly lower percentage of shredding (1.12 ± 0.6%, p < 0.01) compared to the ARP group (3.52 ± 1.6%). Pretreatment with (20 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, and 100 mg/kg) canagliflozin reversed anxiety levels and hyperactivity and reduced hyper-locomotor activity significantly (161 ± 34.9 s, p < 0.05; 154 ± 44.7 s, p < 0.05; 147 ± 33.6 s, p < 0.05) when compared with the VPA group (303 ± 140 s). Moreover, canagliflozin and ARP mitigated oxidative stress status by restoring levels of glutathione (GSH) and catalase (CAT) and increasing the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) in all tested brain regions. The observed results propose repurposing of canagliflozin in the therapeutic management of ASD. However, further investigations are still required to verify the clinical relevance of canagliflozin in ASD.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitors; VPA-induced ASD; aripiprazole; autism spectrum disorder; behavioral assessments; biochemical assays; canagliflozin; oxidative stress biomarkers; rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or other types of competing interests with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Indika N.L., Frye R.E., Rossignol D.A., Owens S.C., Senarathne U.D., Grabrucker A.M., Perera R., Engelen M.P., Deutz N.E. The Rationale for Vitamin, Mineral, and Cofactor Treatment in the Precision Medical Care of Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Pers. Med. 2023;13:252. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020252. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

