Carboxymethylated Gums and Derivatization: Strategies and Significance in Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 37242559
- PMCID: PMC10222150
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16050776
Carboxymethylated Gums and Derivatization: Strategies and Significance in Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering
Abstract
Natural polysaccharides have been widely exploited in drug delivery and tissue engineering research. They exhibit excellent biocompatibility and fewer adverse effects; however, it is challenging to assess their bioactivities to that of manufactured synthetics because of their intrinsic physicochemical characteristics. Studies showed that the carboxymethylation of polysaccharides considerably increases the aqueous solubility and bioactivities of inherent polysaccharides and offers structural diversity, but it also has some limitations that can be resolved by derivatization or the grafting of carboxymethylated gums. The swelling ratio, flocculation capacity, viscosity, partition coefficient, metal absorption properties, and thermosensitivity of natural polysaccharides have been improved as a result of these changes. In order to create better and functionally enhanced polysaccharides, researchers have modified the structures and properties of carboxymethylated gums. This review summarizes the various ways of modifying carboxymethylated gums, explores the impact that molecular modifications have on their physicochemical characteristics and bioactivities, and sheds light on various applications for the derivatives of carboxymethylated polysaccharides.
Keywords: carboxymethylated gums; derivatization; drug delivery; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
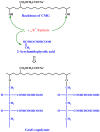
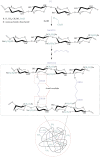
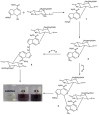
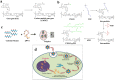

References
-
- Dalei G., Das S. Carboxymethyl guar gum: A review of synthesis, properties and versatile applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2022;176:111433. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111433. - DOI
-
- Khushbu, Warkar S.G. Potential applications and various aspects of polyfunctional macromolecule- carboxymethyl tamarind kernel gum. Eur. Polym. J. 2020;140:110042. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.110042. - DOI
-
- Rai N., Bal T., Swain S. In vitro evaluations of biodegradable polyacrylamide grafted moringa bark gum graft copolymer (MOG-g-PAAM) as biomedical and controlled drug delivery device synthesized by microwave accelerated free radical synthesis. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2020;54:385–396. doi: 10.5530/ijper.54.2.44. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

