The Pillars for Renal Disease Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 37242585
- PMCID: PMC10223945
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051343
The Pillars for Renal Disease Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
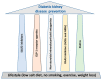
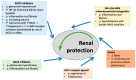
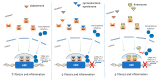
The diabetes epidemic and the increasing number of patients with diabetic chronic vascular complications poses a significant challenge to health care providers. Diabetic kidney disease is a serious diabetes-mediated chronic vascular complication and represents a significant burden for both patients and society in general. Diabetic kidney disease not only represents the major cause of end stage renal disease but is also paralleled by an increase in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Any interventions to delay the development and progression of diabetic kidney disease are important to reduce the associated cardiovascular burden. In this review we will discuss five therapeutic tools for the prevention and treatment of diabetic kidney disease: drugs inhibiting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, statins, the more recently recognized sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists, and a novel non-steroidal selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist.
Keywords: diabetes; kidney disease; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sattar N., Lee M.M.Y., Kristensen S.L., Branch K.R.H., Del Prato S., Khurmi N.S., Lam C.S.P., Lopes R.D., McMurray J.J.V., Pratley R.E., et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9:653–662. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00203-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C.N., Mbanya J.C., et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

