Microneedles: An Emerging Vaccine Delivery Tool and a Prospective Solution to the Challenges of SARS-CoV-2 Mass Vaccination
- PMID: 37242591
- PMCID: PMC10222661
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051349
Microneedles: An Emerging Vaccine Delivery Tool and a Prospective Solution to the Challenges of SARS-CoV-2 Mass Vaccination
Abstract
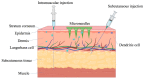
Vaccination is an effective measure to prevent infectious diseases. Protective immunity is induced when the immune system is exposed to a vaccine formulation with appropriate immunogenicity. However, traditional injection vaccination is always accompanied by fear and severe pain. As an emerging vaccine delivery tool, microneedles overcome the problems associated with routine needle vaccination, which can effectively deliver vaccines rich in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) to the epidermis and dermis painlessly, inducing a strong immune response. In addition, microneedles have the advantages of avoiding cold chain storage and have the flexibility of self-operation, which can solve the logistics and delivery obstacles of vaccines, covering the vaccination of the special population more easily and conveniently. Examples include people in rural areas with restricted vaccine storage facilities and medical professionals, elderly and disabled people with limited mobility, infants and young children afraid of pain. Currently, in the late stage of fighting against COVID-19, the main task is to increase the coverage of vaccines, especially for special populations. To address this challenge, microneedle-based vaccines have great potential to increase global vaccination rates and save many lives. This review describes the current progress of microneedles as a vaccine delivery system and its prospects in achieving mass vaccination against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 vaccine; immune response; mass vaccination; microneedles; vaccine delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict financial interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Microneedles: A New Generation Vaccine Delivery System.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Apr 14;12(4):435. doi: 10.3390/mi12040435. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microneedle-Based Vaccine Delivery: Review of an Emerging Technology.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022 Apr 5;23(4):103. doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02250-8. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022. PMID: 35381906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microneedle technology for potential SARS-CoV-2 vaccine delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023 Jun;20(6):799-814. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2023.2209718. Epub 2023 May 8. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 37128730 Review.
-
Microneedles for vaccine delivery: challenges and future perspectives.Ther Deliv. 2017 Jun;8(6):447-460. doi: 10.4155/tde-2017-0032. Ther Deliv. 2017. PMID: 28530151 Review.
-
Implantable microneedles with an immune-boosting function for effective intradermal influenza vaccination.Acta Biomater. 2019 Oct 1;97:230-238. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.07.048. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31362139
Cited by
-
Targeting capacity, safety and efficacy of engineered extracellular vesicles delivered by transdermal microneedles to treat plasmacytoma in mice.Clin Transl Med. 2025 May;15(5):e70327. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70327. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40317915 Free PMC article.
-
Fourth dose of microneedle array patch of SARS-CoV-2 S1 protein subunit vaccine elicits robust long-lasting humoral responses in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Mar 10;129:111569. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111569. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38340419 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in vaccine delivery: harnessing 3D printing for microneedle patch technology.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Mar 27;87(4):2059-2067. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003060. eCollection 2025 Apr. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40212146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Status of Microneedle Array Technology for Therapeutic Delivery: From Bench to Clinic.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;66(12):3415-3437. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00961-2. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37987985 Review.
-
Beyond the Needle: Innovative Microneedle-Based Transdermal Vaccination.Medicines (Basel). 2025 Feb 7;12(1):4. doi: 10.3390/medicines12010004. Medicines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39982324 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Vaccines and Immunization. 2022. [(accessed on 1 December 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/vaccines-and-immunization#tab=tab_1.
-
- SDGs World Health Statistics 2022. [(accessed on 1 December 2022)]. Available online: https://repository.gheli.harvard.edu/repository/11008/
-
- Chong I., Shin S.D.J., Sanoj Rejinold N., Yeu-Chun K. Microneedles for vaccine delivery: Challenges and future perspectives. Ther. Deliv. 2017;8:447–460. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

