Real-World Effectiveness of Four Types of COVID-19 Vaccines
- PMID: 37243089
- PMCID: PMC10224211
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11050985
Real-World Effectiveness of Four Types of COVID-19 Vaccines
Abstract
Background: There is a scarcity of evidence regarding the real-world effectiveness of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines. This was the first study to evaluate the effectiveness of four types of vaccines against asymptomatic and symptomatic infection, and COVID-19 outcomes among the general population.
Methods: This was a matched comparison group quasi-experimental study conducted in Jordan between 1 January and 29 August 2021. In the first part of the study, 1200 fully vaccinated individuals were matched with 1200 unvaccinated control participants. In order to measure vaccine effectiveness, the infection rates of both vaccinated and unvaccinated groups were calculated. The second part of the study included measuring specific anti-SARS CoV-2 immune cells and antibodies.
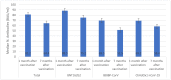
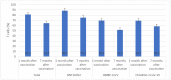
Results: BNT162b2 (Pfizer, New York, NY, USA) showed a significantly higher effectiveness against asymptomatic COVID-19 infection (91.7%) and hospitalization (99.5%) than BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm, Beijing, China) (88.4% and 98.7%, respectively) and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AstraZeneca, Cambridge, UK) (84.3%, and 98.9%, respectively). The effectiveness rates of the Sputnik V (Gamaleya Research Institute, Moscow, Russia) vaccine against asymptomatic, symptomatic, and hospitalization were 100%, 100%, and 66.7%, respectively. The highest median anti-spike (S) IgG values were seen in individuals who received BNT162b2 (2.9 AU/mL) and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (2.8 AU/mL) vaccines. The levels of anti-S IgG were significantly decreased after 7 months of vaccination with BNT162b2 and BBIBP-CorV. There were significant decreases in the median number of neutralizing antibodies one month and seven months after receiving BNT162b2 (from 88.5 to 75.2 4 Bioequivalent Allergen Unit per milliliter/mL), BBIBP-CorV (from 69.5 to 51.5 BAU/mL), and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (from 69.2 to 58.BAU/mL) vaccines. The highest percentage of T cells specific to COVID-19 vaccine was found in individuals who received BNT162b2 (88.5%).
Conclusion: All four vaccines evaluated in this study showed effectiveness against asymptomatic COVID-19 infection, symptomatic infection, hospitalization, and death. Furthermore, BNT162b2, BBIBP-CorV, and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 induced high levels of immunology markers within one month of vaccination.
Keywords: COVID-19; Jordan; delta variant; vaccine effectiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- BBC Will COVID-19 Have a Lasting Impact on the Environment? 2020. [(accessed on 21 December 2020)]. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20200326-covid-19-the-impact-of-coron....
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Selected Adverse Events Reported after COVID-19 Vaccination. [(accessed on 24 December 2021)];2021 Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/safety/adverse-events....
-
- Puranik A., Lenehan P.J., Silvert E., Niesen M.J.M., Corchado-Garcia J., O’horo J.C., Virk A., Swift M.D., Halamka J., Badley A.D., et al. Comparison of two highly-effective mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 during periods of Alpha and Delta variant prevalence. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3902782. - DOI
-
- Blaiszik B., Graziani C., Olds J.L., Foster I. The Delta Variant Had Negligible Impact on COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness in the USA. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.09.18.21263783. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

