The Impact of COVID-19 on People Living with HIV-1 and HIV-1-Associated Neurological Complications
- PMID: 37243203
- PMCID: PMC10223371
- DOI: 10.3390/v15051117
The Impact of COVID-19 on People Living with HIV-1 and HIV-1-Associated Neurological Complications
Abstract
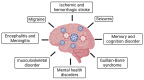
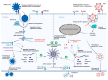
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative pathogen of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a fatal respiratory illness. The associated risk factors for COVID-19 are old age and medical comorbidities. In the current combined antiretroviral therapy (cART) era, a significant portion of people living with HIV-1 (PLWH) with controlled viremia is older and with comorbidities, making these people vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19-associated severe outcomes. Additionally, SARS-CoV-2 is neurotropic and causes neurological complications, resulting in a health burden and an adverse impact on PLWH and exacerbating HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND). The impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 severity on neuroinflammation, the development of HAND and preexisting HAND is poorly explored. In the present review, we compiled the current knowledge of differences and similarities between SARS-CoV-2 and HIV-1, the conditions of the SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 and HIV-1/AIDS syndemic and their impact on the central nervous system (CNS). Risk factors of COVID-19 on PLWH and neurological manifestations, inflammatory mechanisms leading to the neurological syndrome, the development of HAND, and its influence on preexisting HAND are also discussed. Finally, we have reviewed the challenges of the present syndemic on the world population, with a particular emphasis on PLWH.
Keywords: COVID-19; HAND; HIV-1; PLWH; SARS-CoV-2; inflammasomes; microglia; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Update on Central Nervous System Effects of the Intersection of HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2023 Dec;20(6):345-356. doi: 10.1007/s11904-023-00676-8. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2023. PMID: 37950846 Review.
-
Pressing Questions and Challenges in the HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 Syndemic.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021 Aug;37(8):589-600. doi: 10.1089/AID.2021.0005. Epub 2021 Mar 17. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021. PMID: 33587013 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of The Interaction Between HIV Infection And COVID-19: Two Years' Evidence Summary.Front Immunol. 2022 May 10;13:864838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.864838. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35619709 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging COVID-19 Neurological Manifestations: Present Outlook and Potential Neurological Challenges in COVID-19 Pandemic.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Sep;58(9):4694-4715. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02450-6. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34169443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors Associated with Severe COVID-19 and Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome in a Cohort of People Living with HIV on Antiretroviral Treatment and with Undetectable HIV RNA.Viruses. 2022 Feb 28;14(3):493. doi: 10.3390/v14030493. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336900 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Update on Central Nervous System Effects of the Intersection of HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2023 Dec;20(6):345-356. doi: 10.1007/s11904-023-00676-8. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2023. PMID: 37950846 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

