Improved Performance of the QuantiFERON-SARS-CoV-2 Assay with the Extended Set
- PMID: 37243265
- PMCID: PMC10220816
- DOI: 10.3390/v15051179
Improved Performance of the QuantiFERON-SARS-CoV-2 Assay with the Extended Set
Abstract
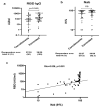
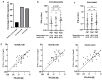
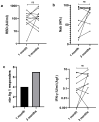
Multiple assays have been developed for the characterization of the functional activation of SARS-CoV-2 specific T-cells. This study was conducted to assess the post-vaccination and post-infection T cell response, as detected by the QuantiFERON-SARS-CoV-2 assay using the combination of three SARS-CoV-2 specific antigens (Ag1, Ag2 and Ag3). An amount of 75 participants with different infection and vaccination backgrounds were recruited for the evaluation of humoral and cellular immune responses. An elevated IFN-γ response in at least one Ag tube was observed in 69.2% of convalescent subjects and 63.9% of vaccinated ones. Interestingly, in a healthy unvaccinated case and three convalescents with negative IgG-RBD, we detected a positive QuantiFERON test after stimulation with Ag3. The majority of the T cell responders reacted simultaneously to the three SARS-CoV-2 specific antigens, and Ag3 demonstrated the highest rate of reactivity. At univariable analysis, the only factor that was associated with an absence of a cellular response was time from blood collection, being less than 30 days (OR:3.5, CI95% [1.15-10.50], p = 0.028). Overall, the inclusion of Ag3 improved the performance of the QuantiFERON-SARS-CoV-2 and showed a particular interest among subjects who fail to achieve a measurable antibody response after infection or vaccination.
Keywords: COVID-19; QuantiFERON-SARS-CoV-2; cellular immunity; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Agrati C., Castilletti C., Goletti D., Meschi S., Sacchi A., Matusali G., Bordoni V., Petrone L., Lapa D., Notari S., et al. Coordinate Induction of Humoral and Spike Specific T-Cell Response in a Cohort of Italian Health Care Workers Receiving BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine. Microorganisms. 2021;9:1315. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061315. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knezevic I., Mattiuzzo G., Page M., Minor P., Griffiths E., Nuebling M., Moorthy V. WHO International Standard for Evaluation of the Antibody Response to COVID-19 Vaccines: Call for Urgent Action by the Scientific Community. Lancet Microbe. 2022;3:e235–e240. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00266-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

